The following section describes how to navigate in notebook-interface-styled editors and perform tasks such as:
To a new code block, you can delete the line of code and enter a new code block, or use Ctrl+Enter to create a new command on which to enter your code block.
Notebook editors add a new command prompt beneath the output, if any, of your previous code block.
Deleting a code block removes the output of that code block.
To re-execute an existing code block, click at the end of the existing code block and use Ctrl+Enter to execute the code block again.
Re-executing a code block removes the output of any later
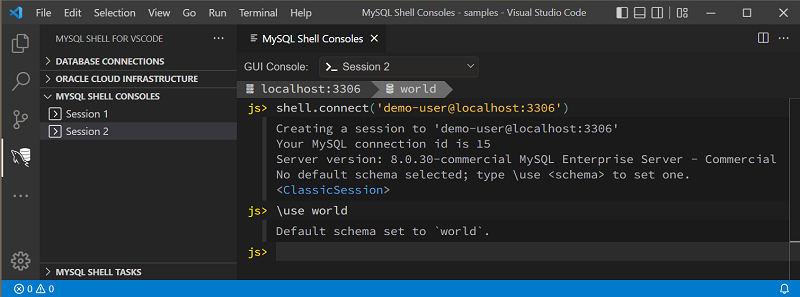
code block. For example, if you issue a
shell.connect method without a schema defined,
then issue a \use world command to use
the world schema. Later, if you highlight the initial
shell.connect method and re-execute it, then
the world schema, you defined later, is removed.
To remove a code block, highlight the code block either using the cursor or right-click, and use Backspace to delete the code block.
To remove the output of an issued code block, use Ctrl+Enter to create a new command prompt beneath the output, you want to delete. Use Ctrl+Backspace to delete the output.
The action of the issued code block is not undone. For
example, if you enter a \use world
command to set the world schema as default. Then, you delete
the output of the use command;
specifically: Default schema set to
`world`. The action is not undone and the schema
defined remains as the world schema.
To execute multiple queries together in SQL mode, each
statement must be terminated with the current delimiter, which
is a semicolon character (;) by default. It
is possible to change the current delimiter value as follows:
sql> DELIMITER new-delimiter
Notebook editors generate a separate tab in the output area
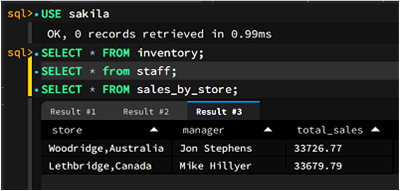
with the result of each statement (if any). For example, the
following figure shows two code blocks. The first block
executes a single, stand-alone query (USE
sakila), which does not require a semicolon. The second
block executes multiple queries together and produces multiple
results (Result #1, Result
#2, and Result #3). Click each
tab to view the output.