Some menu items are not available in the MySQL Workbench Community Edition of this application, and are available only in the MySQL Workbench Commercial Editions. This is indicated where applicable.
Use the menu to open a project, begin a new project, or save a project. The following submenu items apply to the active model tab, EER diagram tab, or both:
: Opens a new MySQL Model tab and closes the tabs of a previously opened model and diagram. The new MySQL Model tab includes an initial schema named
mydbby default. You can rename or remove (and replace) the initialmydbschema. For additional information, see Section 9.1.1.4, “The Physical Schemas Panel”.: Opens a file-selection window with the default file type set to MySQL Workbench (
.mwbfile extension). To display a list of recently opened.mwbfiles, select .: Adds the database objects defined within an existing model file to the active MySQL model and to its diagram, if applicable. This operation also adds a separate diagram icon containing the included objects only to the active model.
: Displays the file path of each model file opened previously. Selecting a file from the list closes the tabs of an open model.
: If selected when the MySQL Model tab is shown, the action closes both the MySQL Model and EER Diagram tabs. However, if the EER Diagram tab is shown, this action closes the EER Diagram tab only. To reopen an
EER Diagramtab, double-click theEER Diagramicon in theModel Overviewsection of theMySQL Modeltab.or : When you save a model, its name appears in the title bar of the application. If you have made changes to a project and have not saved those changes, an asterisk appears in the title bar following the model name. When you save a model, it is saved as a MySQL Workbench file with the
.mwbextension.-
: Imports a MySQL data definition (DDL) script file. For example, this might be a file created by issuing the command mysqldump
--no-data. MySQL Workbench handles the script as follows:If the script does not contain a
CREATE DATABASEstatement, the schema objects are copied to the initial schema, nameddb_name;mydbby default.If the script creates a database, a new tab bearing the database name is added to the
Physical Schemassection of theMySQL Modelpage.If the script contains data, the data is ignored.
For details about importing a DDL script, see Section 9.4.2.1, “Reverse Engineering Using a Create Script”.
: Generates the SQL statements necessary to create a new database or alter an existing one. For more information about these menu items, see Section 9.4.1.1, “Forward Engineering Using an SQL Script”. Use the submenu items to export an EER diagram as a PNG, SVG, PDF, or Postscript file. For an example of a PNG file, see Figure 9.35, “The sakila Database EER Diagram”.
: Enables you to set the paper size, orientation, and margins for printing purposes. This item is enabled only if the EER Diagrams tab is selected.
: Opens a print preview window for the active EER diagram. This item is enabled only if the EER Diagrams tab is selected. For more information, see Section 9.2.1, “Printing Diagrams”.
: Opens print window for the active EER diagram. This item is enabled only if the EER Diagrams tab is selected. For more information, see Section 9.2.1, “Printing Diagrams”.
: Prints the diagram (or diagrams) associated with the active model as a PDF or Postscript file. If your model has multiple diagrams, you can deselect one or more to exclude them from the file, but you must include at least one diagram in the file.
-
: Sets the following properties of your project:
Name: The model document name (default isMySQL Model).Version: The project version number.Author: The project author.Project: The project name.Created: Not editable; determined by the MWB file attributes.Last Changed: Not editable; determined by the MWB file attributes.Description: A description of your project.
: Prompts you to save the current changes and then closes MySQL Workbench.
Use the menu to make changes to objects. The menu item text descriptions change to reflect the name of the selected object.
This menu has items for cutting, copying, and pasting. These actions can also be performed using the Control+X, Control+C, and Control+V key combinations. Undo a deletion using the item. The Control+Z key combination can also be used to undo an operation. It is also possible to carry out a operation using either the menu item, or the key combination Control+Y.
Also find a menu item for removing the currently selected object. The keyboard command for this action is Control+Delete. You can also right-click an object and choose the delete option from the pop-up menu.
The menu item behaves differently depending upon circumstances. For example, if an EER Diagram is active and a table on the canvas is the currently selected object, a dialog box may open asking whether you want to remove the table from the canvas only or from the database as well. For information about setting the default behavior when deleting from an EER Diagram, see Section 3.2.4, “Modeling Preferences”.
If the MySQL Model page is active, the
selected object is deleted from the catalog and there will be
no confirmation dialog box.
Choose to edit the currently selected object. You can also perform edits in a new window by selecting . The keyboard shortcuts for and are Control+E and Control+Shift+E, respectively.
The item has the following submenus:
(Keyboard shortcut, Control+A): Selects all the objects on the active EER diagram.
(Objects of the same type): Finds objects similar to the currently selected object.
: Finds all the objects connected to the currently selected object.
These menu items are active only when an EER Diagram tab is selected. The and the menu items are disabled if no object is currently selected on an EER diagram.
When multiple objects have been selected using one of these menu items, you can navigate between selected items by choosing the or menu item.
Selecting objects changes some of the menu items. If only one object is selected, that object's name appears after the , and menu items. If more than one object is selected, these menu items show the number of objects selected.
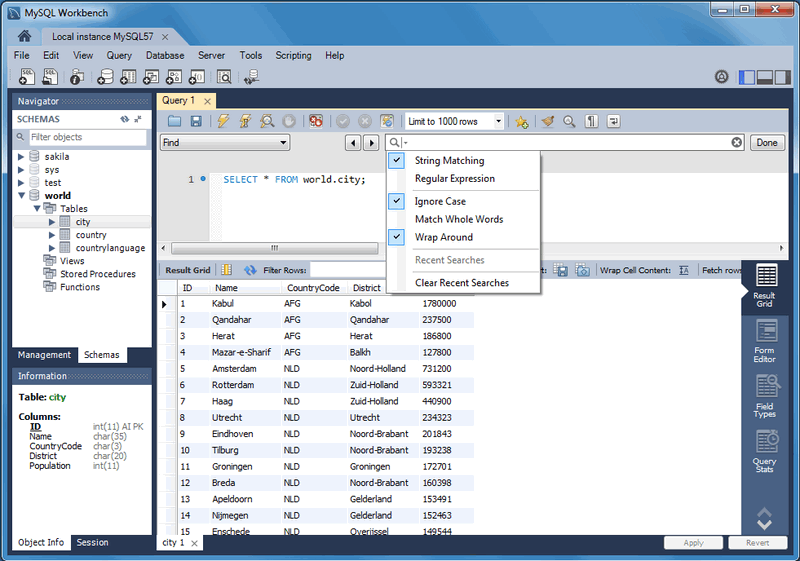
Each MySQL Workbench window includes search functionality. The panel with enabled is shown in the following figure.
The Find dialog options are described in the
following list:
(default) or : Search by matching a string, or a PCRE regular expression.
: A search method that is not case-sensitive. Works with both the and search methods. Enabled by default.
: If enabled, only whole strings are matched. For example, a search for "home" would not match "home_id". Disabled by default.
: The search will wrap around to the beginning of the document, as otherwise it will only search from the cursor position to the end of the document. Enabled by default.
And the arrows jump to the discovered search terms, and behave according to the option.
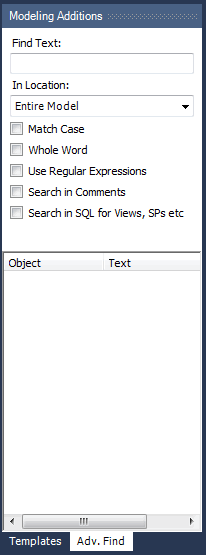
The MySQL Workbench Commercial Editions include an advanced Find facility for models, as indicated in the figure that follows.
You can search the following locations:
Entire Model: Searches the entire model.
Current View: Searches the current view only. This may be the
MySQL Modelpage.All Views: Searches the
MySQL Model Pageand all EER diagrams.Database Objects: Searches database objects only.
Selected Figures: Searches the currently selected objects. This feature works only for EER diagrams.
Enter the text you wish to search for in the Find Text list. You may also select any or all of the following check boxes:
Match Case
Whole Word
Use Regular Expression
Search in Comments
Search in SQL for Views, SPs etc.
Any text you enter into the Find Text list is retained for the duration of your session. Use the or buttons to find occurrences of your search criterion.
Clicking the button opens a Find Results window anchored at the bottom of the application. If you wish, you may undock this window as you would any other.
Use this window to navigate to objects. For example,
double-clicking the Description of an object
located on an EER diagram navigates to the specific diagram and
selects the object. Notice that the properties of the object are
displayed in the Properties palette.
The Find dialog window can also be opened
using the Control+F key combination. Use
Control+G to find the next occurrence and
Control+Shift+G to find a previous occurrence.
Close the Find dialog window by clicking the
in the top right corner or by pressing
the Esc key.
This menu item enables you to set global preferences for the MySQL Workbench application.
For further information, see Section 3.2, “Workbench Preferences”.
This context-aware menu features general options for changing the view in MySQL Workbench. These options change depending on the current tab, and here are the available menu items:
General options:
: Selects the home screen.
: Configure which of the three available panels are open. You may also manage this from the GUI using the panel toggle buttons on the top-right side of MySQL Workbench.
: Displays the console output.
: Selects the next (moves to the right, and wraps around) MySQL Workbench tab.
: Selects the previous (moves to the left, and wraps around) MySQL Workbench tab.
Model/EER options:
: A submenu with items that activate (slide open) specific panels. Designated panels include the "Model Navigator", "Catalog", "Layers", "User Datatypes", "Object Descriptions", "Object Properties", and "Undo History".
: The default level of detail of an EER diagram.
: Zooms in on an EER diagram.
-
: Zooms out from an EER diagram.
The ability to zoom in on an EER diagram is also available using the slider tool in the
Model Navigatorpalette. See Section 9.1.2.3, “The Model Navigator Panel”. : Bookmarks an object. From the keyboard, select the object you wish to bookmark, then use the key combination Control+Shift and the number of the marker (1 through 9). You may create up to nine markers.
: Returns to a marker. From the keyboard, use the Control key and the number of the marker.
: Displays grid lines on an EER diagram.
: Toggles Page Guides to help design the EER diagram on a per-page basis.
The menu items apply only to objects on an EER diagram canvas and are enabled only if an EER diagram view is active. The menu has these items:
: Aligns items on the canvas to the grid lines
: Brings objects to the foreground
: Sends objects to the background
: Centers objects on the canvas
: Automatically arranges objects on the canvas
: Expands an object on an EER diagram. For example, if a table has a long column name that is not fully displayed, this menu item expands the table to make the column visible. This menu item is not enabled unless an object is selected.
: Use this item to expand all objects on an EER diagram. This item will display a table's columns if the object notation supports expansion. Some object notations, such as
Classic, do not permit expansion or contraction. Indexes will not automatically be expanded unless they were previously expanded and have been collapsed using the menu item.: Undo the operation performed by .
When a model is opened, this menu features actions to perform against your model, and the menu has these items:
: Creates a new EER Diagram. The keyboard shortcut is Control+T.
: Creates an EER diagram from all the objects in the catalog.
: Presents a dialog box that enables you to add and delete user defined data types.
: For information about this menu item, see Section 9.1.1.1.5.1, “The DBDoc Model Reporting Dialog Window (MySQL Workbench Commercial)”. MySQL Workbench Commercial only.
: Checks the validity of the model using ANSI standards. For information about this menu item, see Section 9.1.1.1.5.2, “The Validation Submenus (MySQL Workbench Commercial)”. MySQL Workbench Commercial only.
: Checks the validity of the model using MySQL standards. For information about this menu item, see Section 9.1.1.1.5.2, “The Validation Submenus (MySQL Workbench Commercial)”. MySQL Workbench Commercial only.
: For information about this menu item, see Section 9.1.1.1.5.3, “The Object Notation Submenu”.
: For information about this menu item, see Section 9.1.1.1.5.4, “The Relationship Notation Submenu”.
-
: Opens a diagram size dialog box that enables you to adjust the width or height of the canvas. The unit of measure is pages; the default value is two.
When you have tables with numerous columns, use this menu item to increase the size of the EER.
-
: Sets options at the model level. These options should not be confused with the options that are set globally for the Workbench application, and which are referred to as Workbench Preferences. The available model options are a subset of the Workbench Preferences options.
For more information about Workbench Preferences, see Section 3.2.4, “Modeling Preferences”.
This dialog window is found by navigating to the menu and choosing the item.
The feature is only available in MySQL Workbench Commercial.
Use this dialog window to set the options for creating documentation of your database models. For more information, see Section 9.2.2, “DBDoc Model Reporting”.
The menu has two validation submenus, and . Use these submenus for general validation and MySQL-specific validation of the objects and relationships defined in your model.
These items are only available in MySQL Workbench Commercial.
The submenu has these items:
: Performs all available validation checks
: Checks for objects with no content, such as a table with no columns
: Checks the efficiency of tables, such as a table with no primary key defined
: Checks for duplicate identifiers, such as two tables with the same name
: Checks for consistent naming conventions
: Checks, for example, that a foreign key does not reference a nonprimary key column in the source table
The submenu has these items:
: Performs all available validation checks
: Checks for invalid references, such as a table name longer than the maximum permitted
: Checks for correct SQL syntax
: Checks for objects with the same name
For detailed information about validation, see Section 9.2.3, “Schema Validation Plugins”.
The items under the submenu apply to both a model and an EER diagram.
The submenu has these items:
: Displays table columns, indexes, and triggers
: Shows only a table's columns
: Similar to the
Workbench (Simplified)style showing only the table's columns: The ICAM DEFinition language information modeling style
The object notation style that you choose persists for the duration of your MySQL Workbench session and is saved along with your model. When MySQL Workbench is restarted, the object notation reverts to the default.
If you plan to export or print an EER diagram be sure to decide on a notation style first. Changing notation styles after objects have been placed on a diagram can significantly change the appearance of the diagram.
The items under the submenu apply to both a model and an EER diagram.
The submenu has these items:
: The default modeling style. For an example, see Figure 9.30, “Adding Tables to the Canvas”.
: Uses a diamond shape to indicate cardinality.
: Universal Modeling Language style.
: The ICAM DEFinition language information modeling method
To view the different styles, set up a relationship between two or more tables and choose the different menu items.
The relationship notation style that you choose persists for the
duration of your MySQL Workbench session and is saved along with
your model. When MySQL Workbench is restarted, the relationship
notation reverts to the default, the Crow's
Foot style.
If you plan to export or print an EER diagram, be sure to decide on a notation style first. Changing notation styles after objects have been placed on a diagram can significantly change the appearance of the diagram.
This menu features actions against the connected MySQL server. The menu has these items:
: Launches the SQL Editor, which enables you to create SQL code and execute it on a live server. For more information, see Section 8.1, “Visual SQL Editor”.
: Launches the Manage Server Connections dialog, which enables you to create and manage multiple connections. For more information, see Section 5.3, “Manage Server Connections”
: Creates a model from an existing database. For more information, see Section 9.4.2.2, “Reverse Engineering a Live Database”.
: Creates a database from a model. For more information, see Section 9.4.1.2, “Forward Engineering to a Live Server”.
-
: Executes the database migration wizard for MySQL databases. It is useful for moving from an older MySQL server to the latest MySQL version, and is meant for local development purposes. You should not use this tool on production MySQL instances as they often require more complex data migration techniques.
For additional information about this wizard, see MySQL Schema Transfer Wizard.
: Executes the database migration wizard for most any database, and is meant to migrate tables and data from supported database systems to your MySQL server. For additional information, see Chapter 10, Database Migration Wizard.
: From here you can define custom type mappings, such as migrating the source data type
int8to the target MySQL data typeBIGINT.: Synchronizes your database model with an existing database. For more information, see Section 9.5.1, “Database Synchronization”.
: Allows you to compare a target database or script with the open model, external script, or a second database, and apply these changes back to the target. For more information, see Section 9.5.1, “Database Synchronization”.
: Compares your schema model with a live database or a script file. Section 9.5.2, “Compare and Report Differences in Catalogs”.
The menu lists tools and utilities that related to MySQL Workbench usage.
: Launches a file browser to open a specific audit log file. MySQL Workbench prompts for sudo access if the MySQL Workbench user is unable to read the audit log file. For additional information about the Audit Inspector, see Section 6.6, “MySQL Audit Inspector Interface”. MySQL Workbench Commercial only.
: Backup (or restore) your MySQL Connections, as defined in MySQL Workbench. Connection data is stored in a
connections.xmlfile, for additional information about this file, see Section 3.3, “MySQL Workbench Settings and Log Files”.: These utilities generate PHP code to either "Connect to the MySQL server" or "Iterate SELECT results", if applicable. For additional information about PHP code generation, see Section 8.1.11.2, “Generating PHP Code”.
: Opens the mysqluc MySQL Utility. For additional information about MySQL Utilities, see Appendix F, MySQL Utilities.
This menu features GRT scripting and plugin options. The menu has these items:
: Launches the MySQL Workbench Scripting Shell. For additional information, see Section C.5, “The Workbench Scripting Shell”.
: Opens a New Script File dialogue, with options to create a , , or .
: Opens a Open GRT Script dialogue, which defaults to the Workbench scripts directory. Files are opened into the Workbench Scripting Shell window.
: Executes the script that is currently open.
: Executes the specified script file.
: Loads and installs a plugin or module file
: Displays information about the plugins that are installed, and allows disabling and uninstalling the plugins.
Use the menu when you require support, or when you want to help improve MySQL Workbench. This menu has the following items:
: Opens a window showing a local copy of the MySQL Workbench documentation. Read, search, or print the documentation from this window.
: Opens your default browser on the MySQL website home page.
: Opens your default browser on the MySQL Workbench product page.
: Displays information about your system, which is useful when reporting a bug. For more information, see Section 9.1.1.1.9.1, “System Info”.
: Opens your default browser to bugs.mysql.com, and automatically fills in several fields such as the Operating System and MySQL Workbench version by passing in additional data via the GET request. The default "Description" requests you to also attach the Workbench log file. For additional information about reporting useful bug reports, see Appendix D, How To Report Bugs or Problems.
: Opens your default browser to see a list of current bugs.
: Opens up the directory that contains the MySQL Workbench log files.
: Opens up the main MySQL Workbench log file in your default text editor. This file is typically named
wb.log.: Checks if you are using the current MySQL Workbench version. If you are, then a popup informs you of this. If not, then a prompt asks you to open the MySQL Workbench download page.
: Displays the MySQL Workbench
Aboutwindow. This also displays the MySQL Workbench version.
Use the , menu item to display information about your system. This item is especially useful for determining your rendering mode. Sample output follows.
MySQL Workbench Community (GPL) for Windows version 6.1.4 revision 11773 build 1454
Configuration Directory: C:\Users\philip\AppData\Roaming\MySQL\Workbench
Data Directory: C:\Users\philip\Desktop\MySQL\MySQL Workbench 6.1.4 CE
Cairo Version: 1.8.8
OS: Microsoft Windows 7 Service Pack 1 (build 7601), 64-bit
CPU: 4x Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-2400 CPU @ 3.10GHz, 8.0 GiB RAM
Active video adapter NVIDIA GeForce GT 610
Installed video RAM: 1024 MB
Current video mode: 1920 x 1080 x 4294967296 colors
Used bit depth: 32
Driver version: 9.18.13.2049
Installed display drivers: nvd3dumx.dll,nvwgf2umx.dll,nvwgf2umx.dll,nvd3dum,nvwgf2um,nvwgf2um
Current user language: English (United States)