MySQL Workbench provides validation modules so that you can test your models before implementing them.
This functionality is only available in MySQL Workbench Commercial.
The validation (MySQL) plugins are accessed from the
menu within an open MySQL
Model or EER Diagram tab. Beneath the
menu item are a number of specific validation tests. Running any one
of these tests (or ) displays
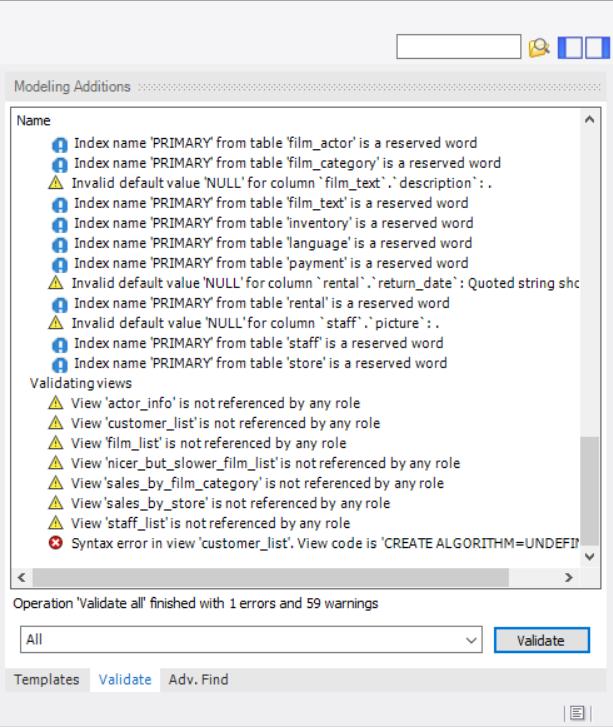
validation output in the Modeling Additions
area of the window (click ![]() from the toolbar to open or close the panel).
Alternatively, you can run the same validation tests from the
Validate tab within the panel as the following
figure shows.
from the toolbar to open or close the panel).
Alternatively, you can run the same validation tests from the
Validate tab within the panel as the following
figure shows.
Information, warning, and error messages include an icon to show the severity of each issue visually. In addition, the output is organized by category: Validating routine groups, Validating routines, Validating tables, and Validating views. Changes made to (see ) may alter the output of the individual validation tests. To copy one or more messages, highlight the output and select from the context menu.
The following list names the validation type and gives examples of specific violations:
-
Consistency Validation
Use of the same column with columns of differing data types
-
Duplicated Identifiers Validation
Duplicate object names
Duplicate role or user names
Duplicate index or routine names
-
Empty Content Validation
A table with no columns
A routine or view with no SQL code defined
A routine group containing no routines
A table, view, or routine not referenced by at least one role
A user with no privileges
Objects such as tables that do not appear on at least one EER Diagram
-
Integrity Violation
An object name longer than the maximum permitted
A foreign key defined for an engine type that does not support foreign keys (not yet implemented)
A view or routine that references a nonexistent table (not yet implemented)
A default value that does not match a column's data type
An invalid partitioning scheme
-
Logic Validation
A foreign key that refers to a column other than the primary key in the source table
Any object that is object is either read only or write only by role definition
Placeholder objects left over from reverse engineering
-
Syntax Violation
A routine, trigger, or view with incorrect SQL syntax
A reserved keyword used as an identifier
Use of an invalid character
-
Table Efficiency Validation
A table with no primary key
A primary key that does not use an integer-based data type
A foreign key that refers to a column with a different data type