Groups organize instances into useful collections. For example, you can create groups for development and production instances. Instances added to each group inherit the Advisors scheduled for that group.
There are two types of group in MySQL Enterprise Monitor: user-defined and replication. User-defined groups are those created and managed in MySQL Enterprise Service Manager's Manage Groups page. An instance can belong to one or more groups.
You can also define groups and add instances to those groups using the MySQL Enterprise Monitor Agent configuration utility. For information, see Agent Connection Utilities. You can use the configuration utility to add connections to existing groups, or to create a group and add a connection to it, but cannot delete an existing group.
Replication groups are instances configured in replication topologies. These groups cannot be managed by MySQL Enterprise Service Manager. MySQL Enterprise Monitor automatically creates groups for replication topologies. That is, if a master-slave(s) relationship is detected, the relevant group is created to contain all members of that topology.
It is not possible to edit replication group membership. Such groups are populated dynamically. The selection boxes are grayed out in Replication groups. It is possible to change the Group Name and Group Description, only.
NDB Cluster and InnoDB cluster topologies are not manageable and are not displayed in the Manage Groups page.
The primary uses for groups are:
Access Control: You can assign users to specific groups. The user sees only those instances in the group to which they have rights. The groups are associated with Roles, and the users are assigned to the roles. For more information, see Chapter 23, Access Control.
Organization: grouping related instances together, in order to ensure consistent Advisor scheduling and event generation. An instance can belong to multiple groups. It is not possible for instances involved in a replication topology to belong to multiple groups.
To create groups, the user must be assigned to a role with the New Group Creation permission set to Administer. To view groups, they must have the Server Group permission set to at least Read-Only.
To open the Groups page, click the Groups link on the Settings menu.
To create a group, do the following:
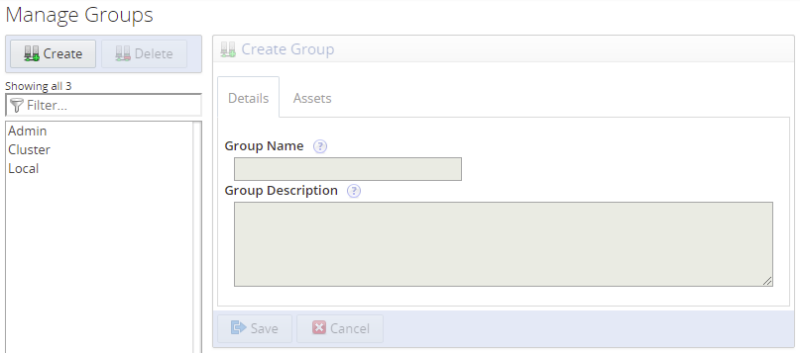
Click Create. The Create Group frame is activated.
Define a Group Name and a Description.
It is possible to create empty groups, and add the instances later, or to allow the Agent installations to add the instances to the groups by adding the group name to the Monitor Group field in the installer.
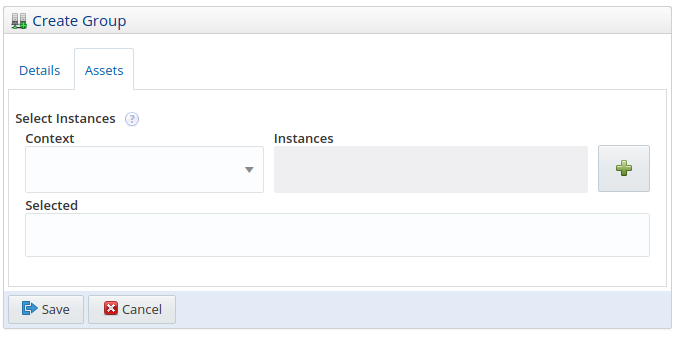
To add instances to the group, select the Assets tab.
Select the required instances by selecting a context. It is not possible to select instances without selecting a context.
Select All to make all instances available for selection in the Instances field. To filter further, select any of the existing groups to make their contents available in the Instances field.
Select an instance by clicking in the Instances field and selecting the required instances. This field also supports auto-complete.
Click the add button to add your selection to the Selected field.
Click Save to save your new group. Click Cancel to discard your changes.
To edit a group, select it in the list, and edit as required.
NoteEditing groups requires the user be assigned to a Role with the Server Group and MySQL Instances permissions set to Administer.