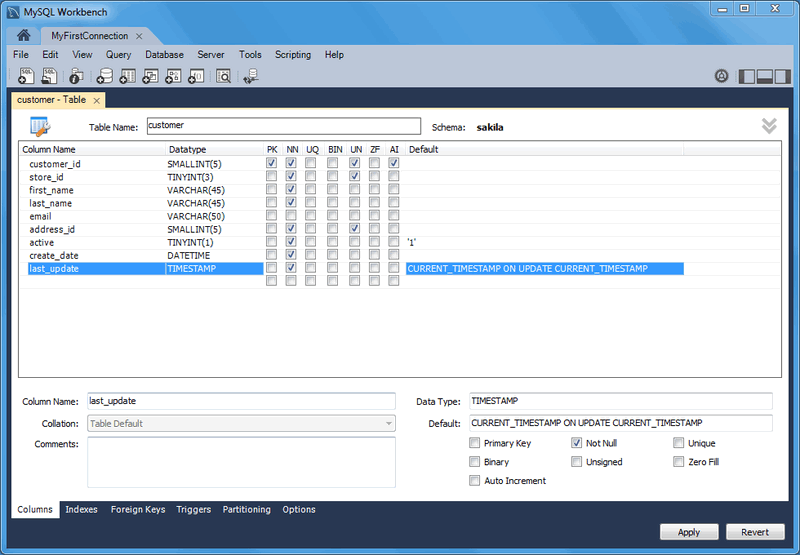
Use the Columns subtab to display and edit all the column information for a table. With this subtab, you can add, drop, and alter columns.
You can also use the Columns subtab to change column properties such as name, data type, and default value. The following figure shows an example of the Columns subtab.
Right-click a row under the Column Name column
to open a pop-up menu with the following items:
: Move the selected column up.
: Move the selected column down.
: Copies the column for a model.
: Copies and then deletes the column for a model.
: Pastes the column. If a column with the same name already exists, then
_copy1is appended to the column name.: Select multiple contiguous columns by right-clicking and pressing the Shift key. Use the Control key to select separated columns.
: Update all information in the Columns subtab.
: Clear the assigned default value.
: Set the column default value to
NULL.: Set the column default value to
0.: Available for
TIMESTAMPdata types.: Available for
TIMESTAMPdata types.
To add a column, click the Column Name field in
an empty row and enter an appropriate value. Select a data type
from the Datatype list. Select the column
property check boxes as required according to the list of column
properties that follow. For a description of each item, see
CREATE TABLE.
PK: PRIMARY KEY
NN: NOT NULL
UQ: UNIQUE INDEX
BIN: BINARY
UN: UNSIGNED
ZF: ZEROFILL
AI: AUTO_INCREMENT
-
G: Generated Column
This option is available as of MySQL Server 5.7.
To change the name, data type, default value, or comment of a column, double-click the value to edit it.
You can also add column comments to the Column
Comment field. It is also possible to set the column
collation, using the list in the Column
Details panel.
To the left of the column name is an icon that indicates whether
the column is a member of the primary key. If the icon is a small
key, that column belongs to the primary key, otherwise the icon is
a blue diamond or a white diamond. A blue diamond indicates the
column has NN set. To add or remove a column
from the primary key, double-click the icon. You can also add a
primary key by checking the PRIMARY KEY check
box in the Column Details section of the table
editor.
If you wish to create a composite primary key you can select multiple columns and check the PK check box. However, there is an additional step that is required, you must click the Indexes tab, then in the Index Columns panel you must set the desired order of the primary keys.
When entering default values, in the case of
CHAR and VARCHAR data
types MySQL Workbench will attempt to automatically add quotation
marks, if the user does not start their entry with one. For
other data types the user must manage quoting if required, as it
will not be handled automatically by MySQL Workbench.
Care must be taken when entering a default value for
ENUM columns because a non-numeric default
will not be automatically quoted. You must manually add single
quote characters for the default value. Note that MySQL Workbench
will not prevent you from
entering the default value without the single quotation marks.
If a non-numeric default value is entered without quotation
marks, this will lead to errors. For example, if the model is
reverse engineered, the script will contain unquoted default
values for ENUM columns and will fail if an
attempt is made to run the script on MySQL Server.
ENUM, BIT, and SET must contain at least one value when entering these data types into MySQL Workbench.