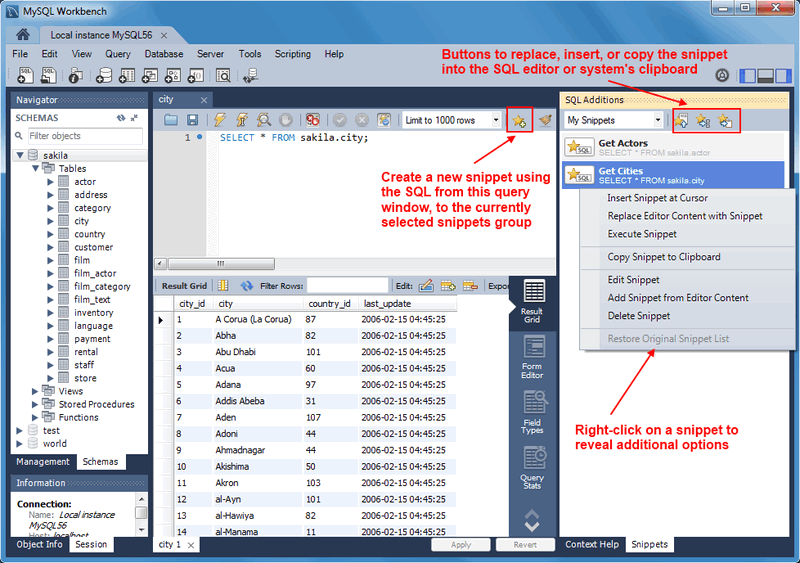
The Snippets secondary tab includes built-in, local, and shared custom snippets. The My Snippets option stores custom snippets in a file under the MySQL Workbench user's configuration directory. Select the Shared option for shared snippets.
Snippets can be inserted into the SQL editor or the system's clipboard. To insert (use) a snippet, either use the snippet icons or right-click on the desired snippet and choose Insert. The next figure shows the location of the main action icons to use with snippets.
Local snippets are stored in the MySQL Workbench directory. By
default, the My Snippets SQL snippets are
stored as indicated in the following table.
Table 8.1 Default Local Snippet File Location
| Operating System | File Path |
|---|---|
| Windows | %AppData%\MySQL\Workbench\User Snippets.txt |
| macOS | ~username/Library/Application Support/MySQL/Workbench/snippets/User Snippets.txt |
| Linux | ~username/.mysql/workbench/snippets/User Snippets.txt |
Editing (or adding) snippets to My Snippets
in MySQL Workbench edits this plain text file. Optionally, you can
edit this file outside of MySQL Workbench or create new files that
will also be listed under the snippets selector. For example,
adding a file named "More Snippets.txt" will add a "More
Snippets" section to the snippets selection box.
Shared snippets are saved in a
.mysqlworkbench schema on the connected
MySQL server. Selecting "Shared" for the first time will
request permission for MySQL Workbench to create this shared
.mysqlworkbench schema. Users connected to
this MySQL server are allowed to create, edit, and use these
shared snippets.
Shared snippets were added in MySQL Workbench 6.2.0.
The .mysqlworkbench schema is hidden from
within MySQL Workbench as it is considered an internal schema that
does not need to be seen or edited.
Several built-in SQL snippets are bundled with MySQL Workbench, and typically show the SQL syntax for MySQL operations. They are divided up into the following categories.
DB Mgmt (Database Management): Syntax examples use
SHOWin many forms to provide information about databases, tables, columns, or status information about the MySQL server.SQL DDL (SQL Data Definition Language): Syntax examples include creating, altering, and dropping tables, indexes, views, and procedures.
SQL DML (SQL Data Manipulation Language): Syntax examples for operations such as SELECT, INSERT, and REPLACE.
The built-in operations are stored in text files in the same directory as the custom snippet files.
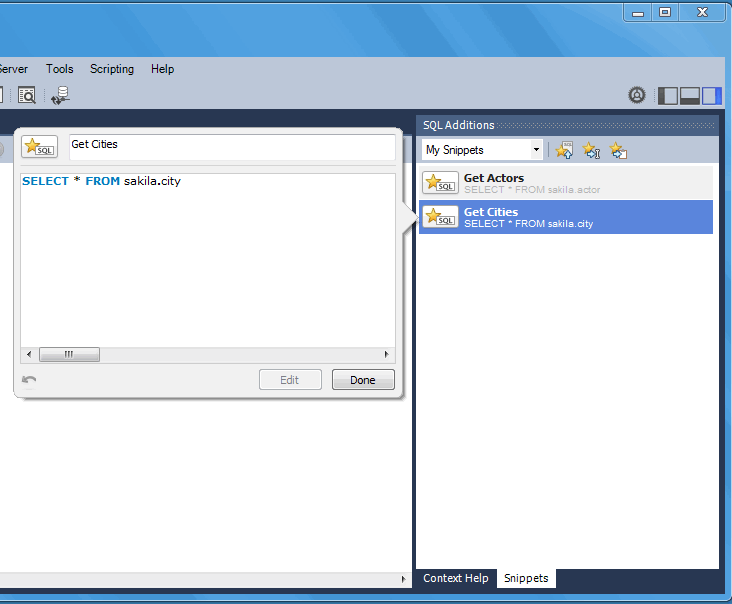
To save a snippet, choose the Snippets Insert icon
(![]() ) or right-click in the snippet window and
choose from the context-menu. Double-click a
snippet to open it, and choose the snippet editor to edit its
body or title. The example in the following figure shows two
snippets with only the first having defined a name.
) or right-click in the snippet window and
choose from the context-menu. Double-click a
snippet to open it, and choose the snippet editor to edit its
body or title. The example in the following figure shows two
snippets with only the first having defined a name.