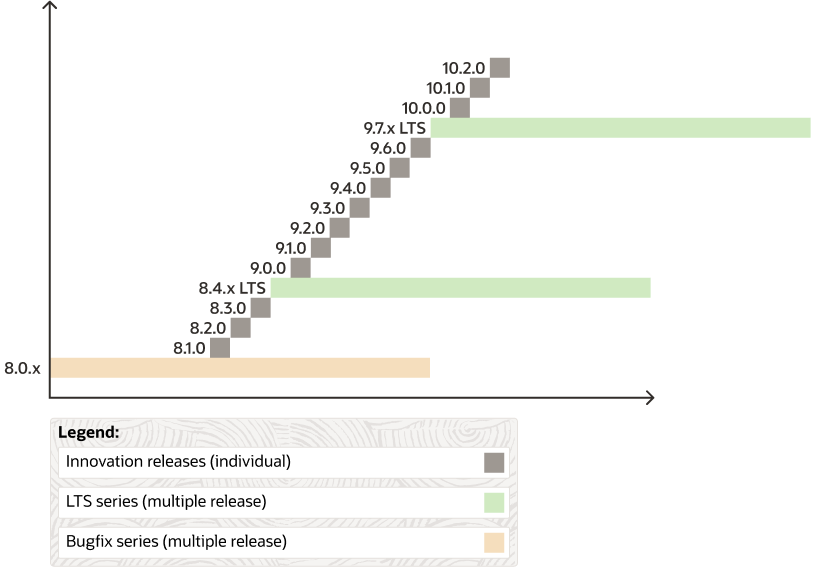
The MySQL release model is divided into two main tracks: LTS (Long-Term Support) and Innovation. All LTS and Innovation releases include bug and security fixes, and are considered production-grade quality.
Audience: If your environment requires a stable set of features and a longer support period.Behavior: These releases only contain necessary fixes to reduce the risks associated with changes in the database software's behavior. There are no removals within an LTS release. Features can be removed (and added) only in the first LTS release (such as 8.4.0 LTS) but not later.Support: An LTS series follows the Oracle Lifetime Support Policy, which includes 5 years of premier support and 3 years of extended support.
Audience: If you want access to the latest features, improvements, and changes. These releases are ideal for developers and DBAs working in fast-paced development environments with high levels of automated tests and modern continuous integration techniques for faster upgrade cycles.Behavior: Apart from new features in innovation releases, behavior changes are also expected as code is refactored, deprecated functionality is removed, and when MySQL is modified to behave more in line with SQL Standards. This will not happen within an LTS release.Behavior changes can have a big impact, especially when dealing with anything application-related, such as SQL syntax, new reserved words, query execution, and query performance. Behavior changes might require application changes which can involve considerable effort to migrate. We intend to provide the necessary tools and configuration settings to make these transitions easier.
Support: Innovation releases are supported until the next Innovation release.
MySQL Server, MySQL Shell, MySQL Router, MySQL Operator for Kubernetes, and MySQL NDB Cluster have both Innovation and LTS releases.
MySQL Connectors have one release using the latest version number but remain compatible with all supported MySQL Server versions. For example, MySQL Connector/Python 9.0.0 is compatible with MySQL Server 8.0, 8.4, and 9.0.
Having two tracks affects how MySQL is installed, upgraded, and downgraded. Typically you choose one particular track and all upgrades progress accordingly.
When using the official MySQL repository, the desired track is
defined in the repository configuration. For example, with
Yum choose
mysql-innovation-community to install and
upgrade Innovation releases or
mysql-8.4-lts-community to
install and upgrade MySQL 8.4.x releases.
LTS Notes
Functionality remains the same and data format does not change in an LTS series, therefore in-place upgrades and downgrades are possible within the LTS series. For example, MySQL 8.4.0 can be upgraded to a later MySQL 8.4.x release. Additional upgrade and downgrade methods are available, such as the clone plugin.
Upgrading to the next LTS series is supported, such as 8.4.x LTS to 9.7.x LTS, while skipping an LTS series is not supported. For example, 8.4.x LTS can't skip 9.7.x LTS to directly upgrade to 10.7.x LTS.
Innovation Notes
An Innovation installation follows similar behavior in that an Innovation release upgrades to a more recent Innovation series release. For example, MySQL 9.0.0 Innovation would upgrade to MySQL 9.3.0.
The main difference is that you cannot directly upgrade between an Innovation series of different major versions, such as 8.3.0 to 9.0.0. Instead, first upgrade to the nearest LTS series and then upgrade to the following Innovation series. For example, upgrading 8.3.0 to 8.4.0, and then 8.4.0 to 9.0.0, is a valid upgrade path.
To help make the transition easier, the official MySQL repository treats the first LTS release as both LTS and Innovation, so for example with the Innovation track enabled in your local repository configuration, MySQL 8.3.0 upgrades to 8.4.0, and later to 9.0.0.
Innovation release downgrades require a logical dump and load.
Additional Information and Examples
For additional information and specific example supported scenarios, see Section 3.2, “Upgrade Paths” or Chapter 4, Downgrading MySQL. They describe available options to perform in-place updates (that replace binaries with the latest packages), a logical dump and load (such as using mysqldump or MySQL Shell's dump utilities), cloning data with the clone plugin, and asynchronous replication for servers in a replication topology.