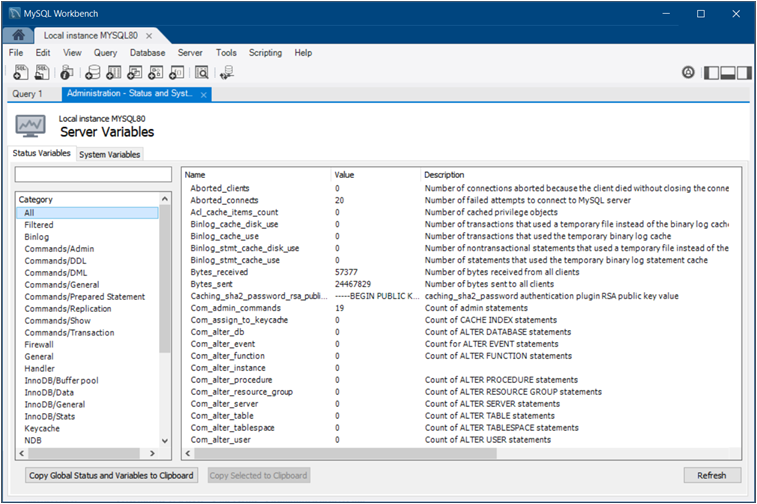
The Administration - Status and System Variables secondary tab lists the full set of server variables for the active MySQL connection. You may also copy all or selected variables to your clipboard.
You can open this secondary tab from either the Navigator area (see MANAGEMENT) or by clicking and then from the menu. The following figure shows the Status Variables subtab selected with all of the status variable listed by name. Each variable has a value, if applicable, and a description.
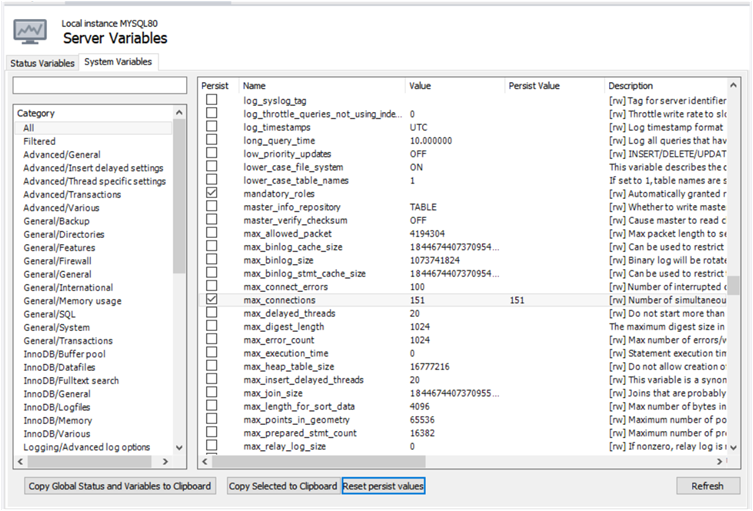
The next figure shows the System Variables
subtab selected with all of the global system variables for the
active server listed by name. You can refine the list of status
and system variables by typing the variable name into to the text
box provided or by selecting a category, such as
InnoDB/General.
Persist System Variables
Beginning with MySQL Workbench 8.0.11, you can set one or more global system variables to persist across server restarts. To persist a variable, select the Persist check box next to the name (see the previous figure). For system variables that include a value, the value is displayed in the Persisted Value column of the list after you select the check box. If a variable is not eligible to be persisted, an informational dialog box appears when you select the check box.
To reset a persistent global system variable, deselect the individual check box and then confirm the reset action for the individual variable in the dialog box that opens. To reset all the persistent variables at once, click and then confirm the reset action for all of the persistent variables.
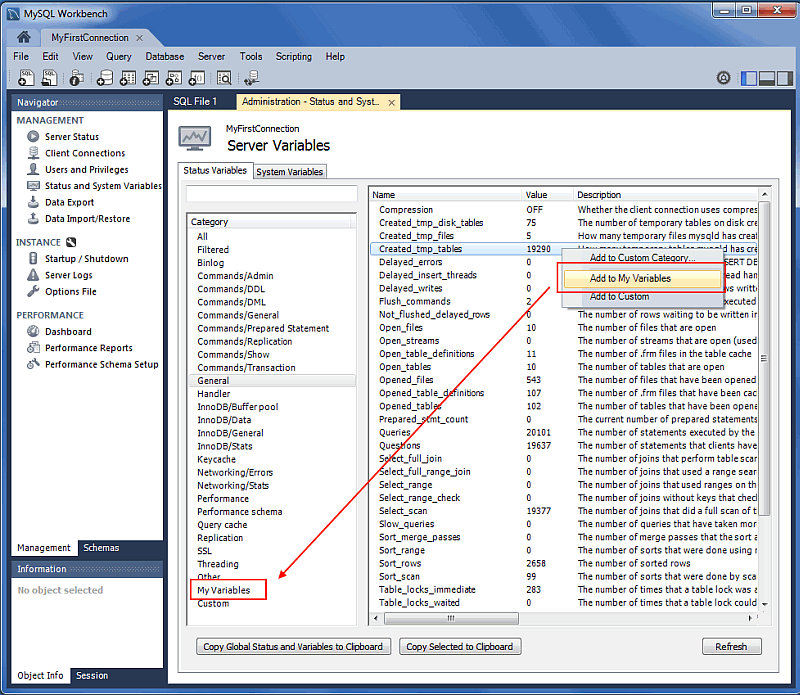
Custom Variable Grouping
The status and system variables are each categorized by groups (such as InnoDB or Logging), and you may also create your own custom groups. Right-click a variable, choose the custom group (or create a new one), and then add the variable to the aforementioned group. Your custom groups are listed along with the pre-existing groups.
The following figure shows an example of a custom group titled
My Variables, which is being added to the
Created_tmp_variables variable.