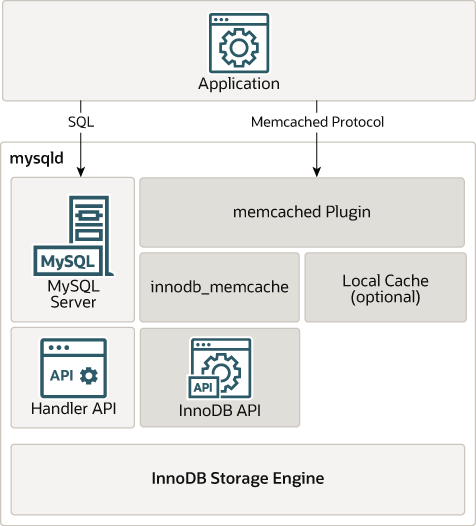
The InnoDB memcached plugin
implements memcached as a MySQL plugin daemon
that accesses the InnoDB storage engine
directly, bypassing the MySQL SQL layer.
The following diagram illustrates how an application accesses data
through the daemon_memcached plugin, compared
with SQL.
Features of the daemon_memcached plugin:
memcached as a daemon plugin of mysqld. Both mysqld and memcached run in the same process space, with very low latency access to data.
Direct access to
InnoDBtables, bypassing the SQL parser, the optimizer, and even the Handler API layer.Standard memcached protocols, including the text-based protocol and the binary protocol. The
daemon_memcachedplugin passes all 55 compatibility tests of the memcapable command.Multi-column support. You can map multiple columns into the “value” part of the key-value store, with column values delimited by a user-specified separator character.
By default, the memcached protocol is used to read and write data directly to
InnoDB, letting MySQL manage in-memory caching using theInnoDBbuffer pool. The default settings represent a combination of high reliability and the fewest surprises for database applications. For example, default settings avoid uncommitted data on the database side, or stale data returned for memcachedgetrequests.Advanced users can configure the system as a traditional memcached server, with all data cached only in the memcached engine (memory caching), or use a combination of the “memcached engine” (memory caching) and the
InnoDBmemcached engine (InnoDBas back-end persistent storage).
Control over how often data is passed back and forth between
InnoDBand memcached operations through theinnodb_api_bk_commit_interval,daemon_memcached_r_batch_size, anddaemon_memcached_w_batch_sizeconfiguration options. Batch size options default to a value of 1 for maximum reliability.The ability to specify memcached options through the
daemon_memcached_optionconfiguration parameter. For example, you can change the port that memcached listens on, reduce the maximum number of simultaneous connections, change the maximum memory size for a key-value pair, or enable debugging messages for the error log.The
innodb_api_trx_levelconfiguration option controls the transaction isolation level on queries processed by memcached. Although memcached has no concept of transactions, you can use this option to control how soon memcached sees changes caused by SQL statements issued on the table used by the daemon_memcached plugin. By default,innodb_api_trx_levelis set toREAD UNCOMMITTED.The
innodb_api_enable_mdloption can be used to lock the table at the MySQL level, so that the mapped table cannot be dropped or altered by DDL through the SQL interface. Without the lock, the table can be dropped from the MySQL layer, but kept inInnoDBstorage until memcached or some other user stops using it. “MDL” stands for “metadata locking”.