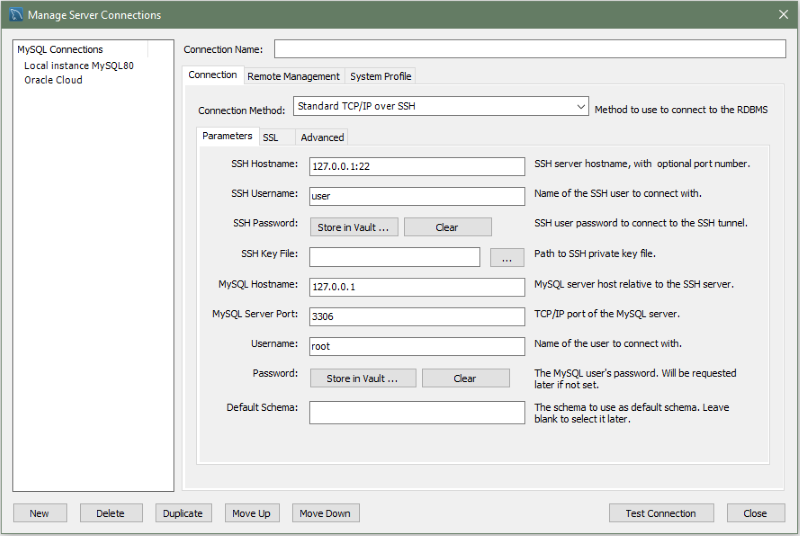
This connection method enables MySQL Workbench to connect to MySQL Server using TCP/IP over an SSH connection.
Parameters Tab
In addition to a number of parameters that are in common with Standard TCP/IP connections, this connection method features a number of specialized parameters. These options are:
SSH Hostname: The name of the SSH server. An optional port number can also be provided. For example,
localhost:22.SSH Username: The name of the SSH user to use to make a connection.
SSH Password: The SSH password. It is recommended that an SSH key file is also used.
-
SSH Key File: A path to the SSH key file.
NoteMySQL Workbench does not accept default PuTTY keys directly. You can convert an existing PuTTY Private Key (ppk) file to OpenSSH format by using the PuTTY Key Generator (PuTTYGen) utility.
If a remote host is missing from the system's list of known hosts, a prompt requires you to confirm the host's fingerprint before storing it. If your stored host fingerprint is different than the host's current fingerprint, then an error is generated and you will be required to handle the discrepancy from outside of MySQL Workbench before creating the connection.
On Linux and macOS, SSH host fingerprints are stored in
~/.ssh/known_hosts. On Microsoft Windows,
they are stored in a file created by MySQL Workbench under the user's
folder, such as
C:\Users\
The path to the SSH known hosts file is configurable (see
Section 3.2.6, “SSH Preferences”).
username\.ssh\known_hosts.
The following figure shows the initial settings of a new connection using the Standard TCP/IP over SSH connection method.
SSL Tab
The SSL options for this connection method are the same as
Standard TCP/IP (see
SSL Tab).
Advanced Tab
The advanced options for this connection method are similar to
Standard TCP/IP (see
Advanced Tab). The
Timeout option does not apply to this
connection method.