Clicking the [+] icon from the home screen launches the Setup New Connection wizard. The wizard provides a MySQL connection form to create a new MySQL connection, and includes a option as a step-by-step approach to creating a new MySQL server connection.
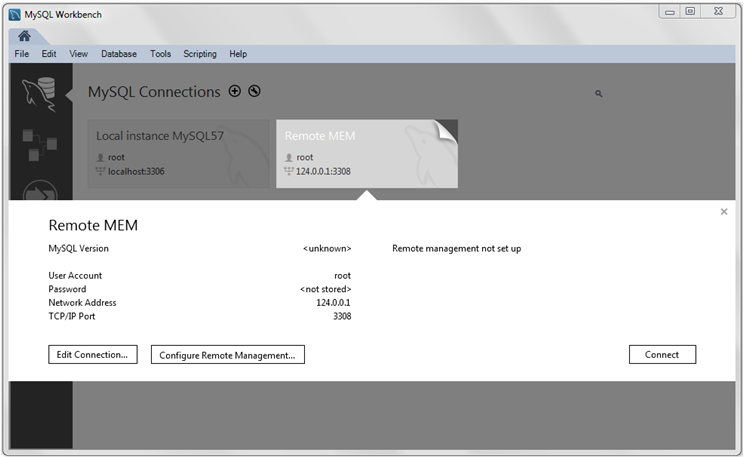
This option can also be executed later (on remote connections) from the home screen by clicking the top right corner of a MySQL remote connection, as the following figure shows.
Executing this wizard is required to perform tasks requiring shell access to the host. For example, starting/stopping the MySQL instance and editing the configuration file.
For a tutorial that demonstrates the following general steps, see Section 5.2, “Creating A New MySQL Connection (Tutorial)”.
The steps presented in the wizard are:
-
Test DB Connection
On this page, MySQL Workbench tests your database connection and displays the results. If an error occurs, click to view the related logs.
-
Management and OS
Used to specify a remote management type and target operating system, which is available when the Host Machine is defined as a remote host.
The SSH login based management option includes configuration entries for the Operating System and MySQL Installation Type.
-
SSH Configuration
If you specified a Remote Host on the Specify Host Machine page, you will be presented with the Host SSH Connection page, that enables you to use SSH for the connection to the server instance. This facility enables you to create a secure connection to remotely administer and configure the server instance. You must enter the host name and user name of the account that will be used to log in to the server for administration and configuration activities. If you do not enter the optional SSH Key for use with the server, then you will be prompted for the password when the connection is established by MySQL Workbench.
NoteThis connection is to enable remote administration and configuration of the MySQL Server itself. It is not the same as the connection used to connect to a server for general database manipulation.
NoteYou must use an SSH connection type when managing a remote server if you wish to start or stop the server or edit its configuration file. Other administrative functions do not require an SSH connection.
-
Windows Management
If a Windows server is used, then setting the Windows configuration parameters is mandatory. Windows management requires a user account with the required privileges to query the system status, and to control services. And read/write access to the configuration file is needed to allow editing of the file.
-
Test Settings
The wizard now attempts a connection to your server and reports the results. If an error occurs, click to view the related logs.
MySQL Workbench must know where the MySQL Server configuration file is located to be able to display configuration information. The wizard is able to determine the most likely location of the configuration file, based on the selection made on the Operating System page of the wizard. However, it is possible to test that this information is correct by clicking the and buttons. The wizard then reports whether the configuration file and server configuration section can in fact be accessed. It is also possible to manually enter the location of the configuration file, and the section pertaining to MySQL Server data; these manually entered values should be tested using the buttons provided. Click the button to continue.
-
Review Settings
The modified settings may be reviewed, which also includes the default values. Select the Change Parameters check box if the MySQL Config File section will be edited, and then click to continue.
-
MySQL Config File
Allows configuration of the MySQL server version. It also allows the editing and validation of the configuration file path, and validation of the server instance section. Click to continue.
-
Specify Commands
Optionally set the commands required to start, stop, and check the status of the running MySQL server instance. Commands can be customized, if required, but the defaults are suitable in most cases. The defaults depend on the selected options on the Operating System page of the wizard. Click to continue.
-
Complete Setup
Name the MySQL server instance on the final step. This name is used throughout MySQL Workbench as a reference to this MySQL connection. After setting a suitable name, click to save the instance.