This section summarizes many of the new features added to MySQL Workbench 6.0, in relation to the MySQL Workbench 5.2 release.
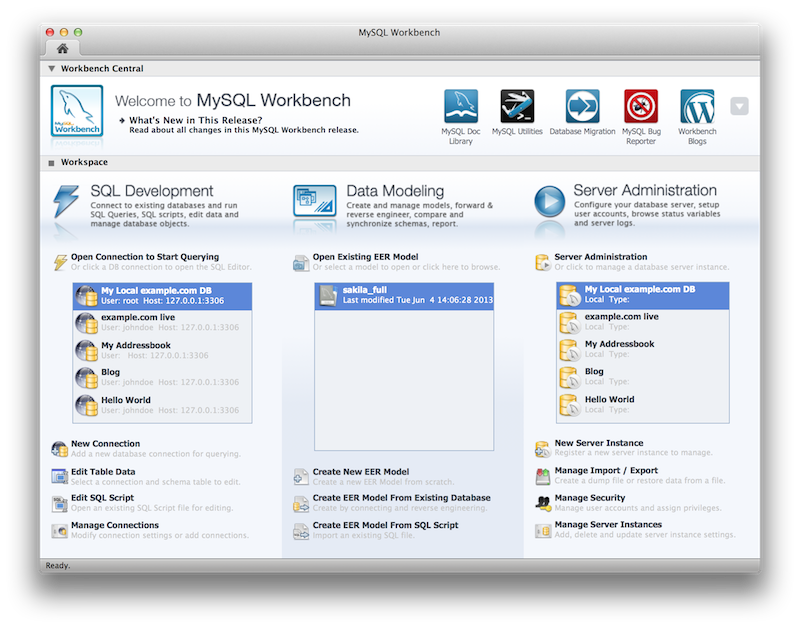
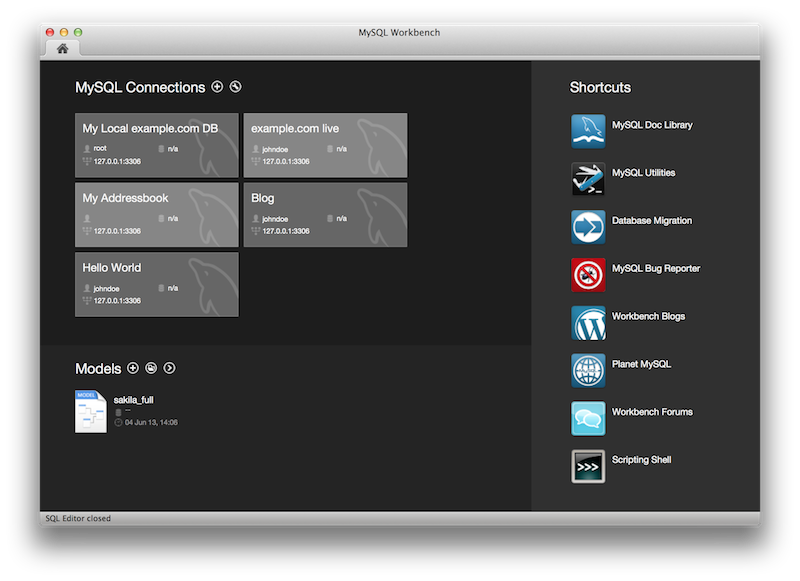
A new, modernized home screen where major functionality of MySQL Workbench can be accessed, including connections to MySQL servers, modeling, migration, and the command-line utilities.
In the new user interface, the Server Administration functionality (such as start/stop server, managing user accounts etc) is now accessible directly from the SQL Editor interface, located near where the schema information can be browsed and queries executed.
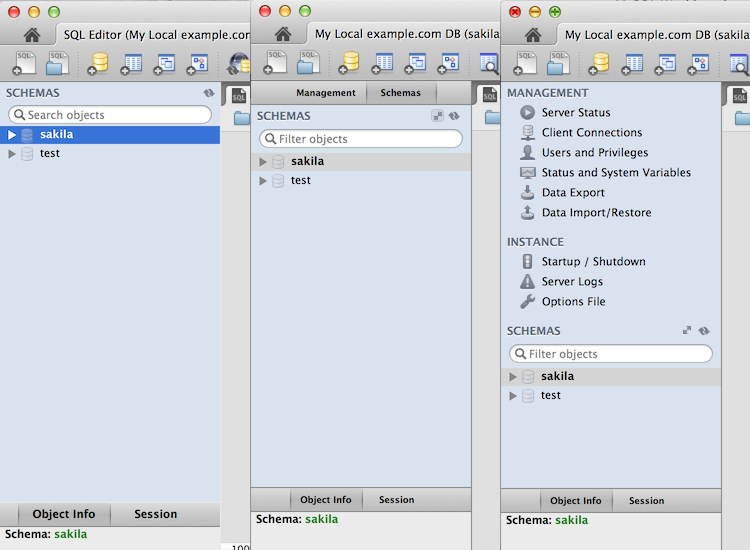
The following figure contains three screenshots of the Schema window in the SQL Editor. The first is from MySQL Workbench 5.2, the second is MySQL Workbench 6.0 with the management tab collapsed, and the third shows what the merged management tab looks like. Toggle the merged and tabbed views by clicking the new merge button next to the refresh button.
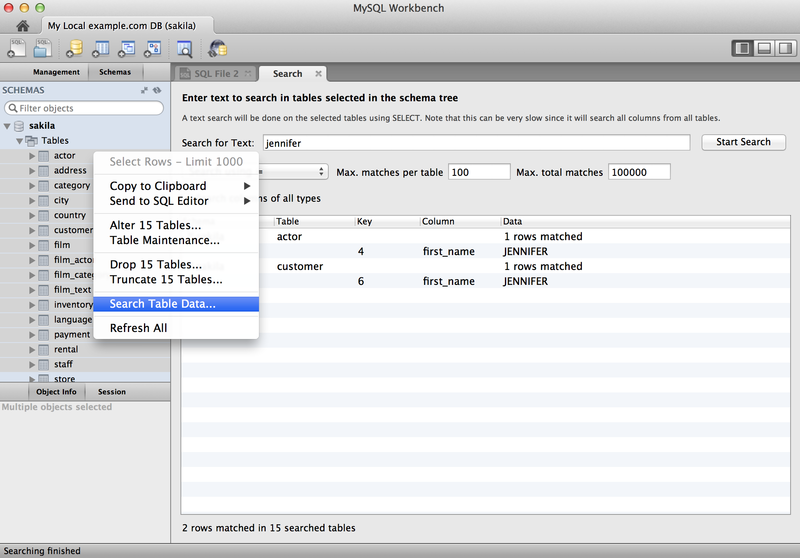
You can select schemas, tables, or both to perform client-side searches for user specified strings and patterns. To access this new search feature, right click select a schema or a table in the left sidebar and select .
This screenshot demonstrates the search feature, along with an example search. Multiple tables were selected and searched in this example:
For additional information, see Section 8.1.8, “Table Data Search Tab”.
Select a keyword or function in your query and after a delay it will show formatted help information from the MySQL Server (equivalent to using the help command from the command-line MySQL Client).
For additional information, see Section 8.1.6, “SQL Additions - Context Help Tab”.
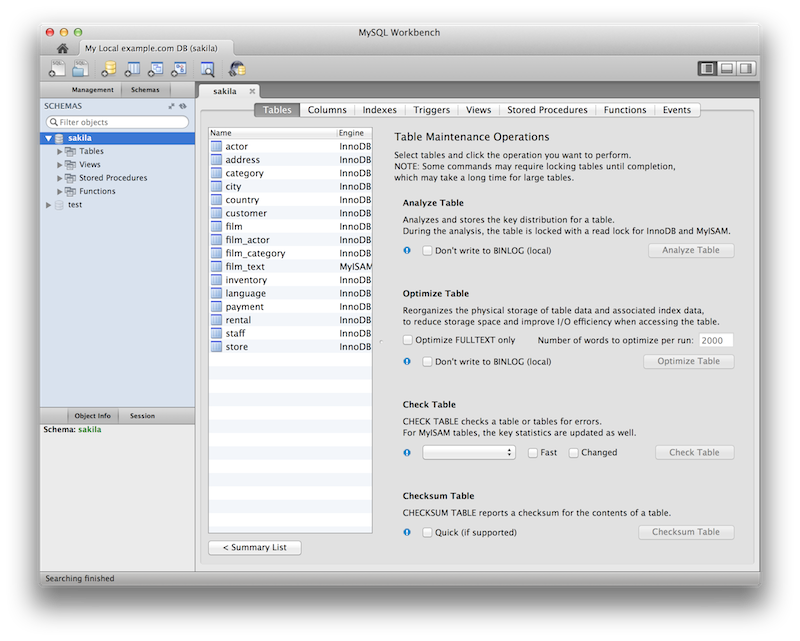
New Schema Inspector feature allows you to browse general
information from schema objects. For tables, it's also
possible to perform maintenance tasks such as
ANALYZE, OPTIMIZE,
CHECK, and CHECKSUM
TABLE. To access the inspector, right-click a schema
and select the
And choosing for a table:
For additional information, see Schema Inspector.
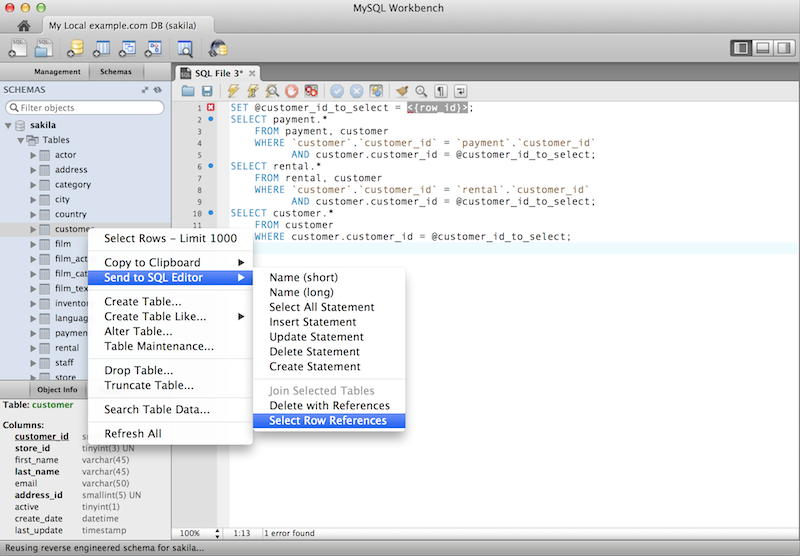
You can generate a series of DELETE
statements needed to delete a row from that table, which
includes rows from other tables that reference it,
recursively. The SELECT version allows you
to preview what rows would be deleted. Right click a table and
select ,
.
Define templates of tables with commonly used columns, to be used to create new tables in a live connection or in an EER model. In the SQL Editor, choose Create Table Like, or in Modeling, use the right sidebar. For additional information, see Section 9.6, “Table Templates”.
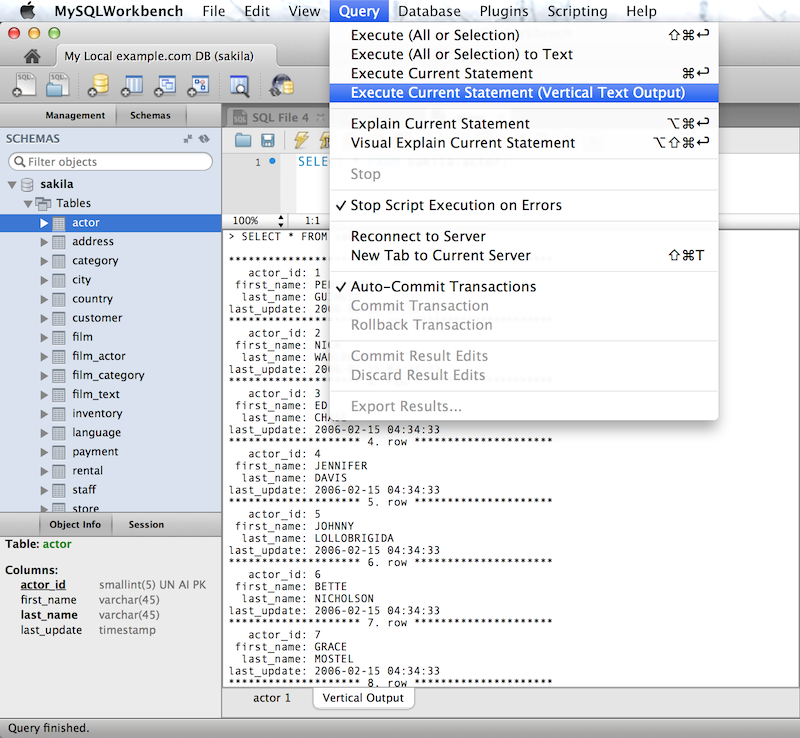
A Vertical Text output option for queries (equivalent to \G from the command-line Client) was added. To execute, choose , .
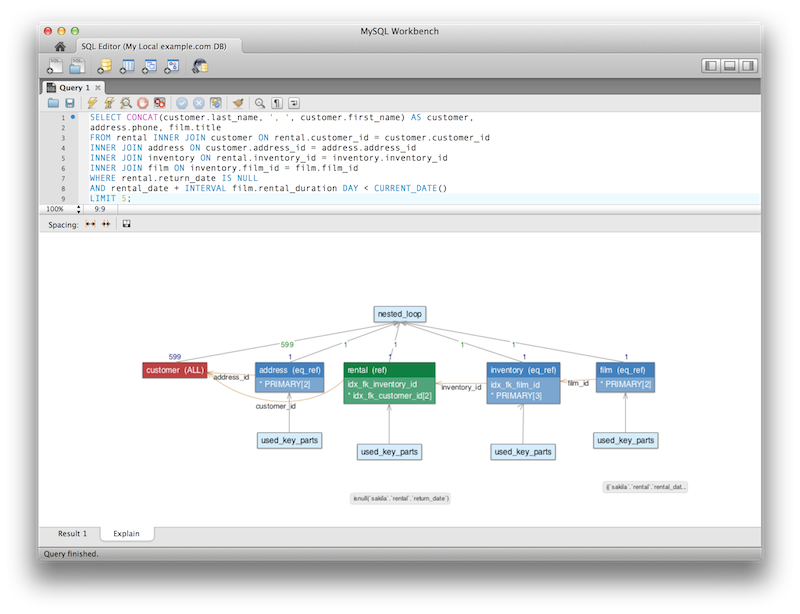
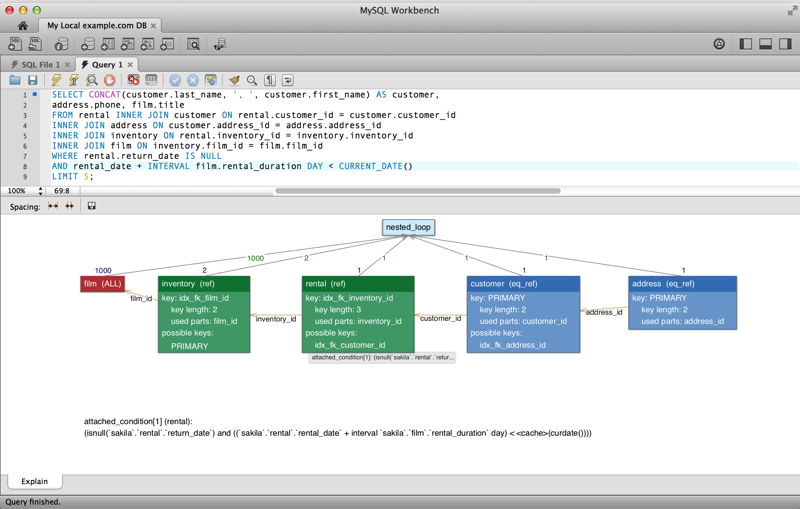
The Visual Explain output was improved.
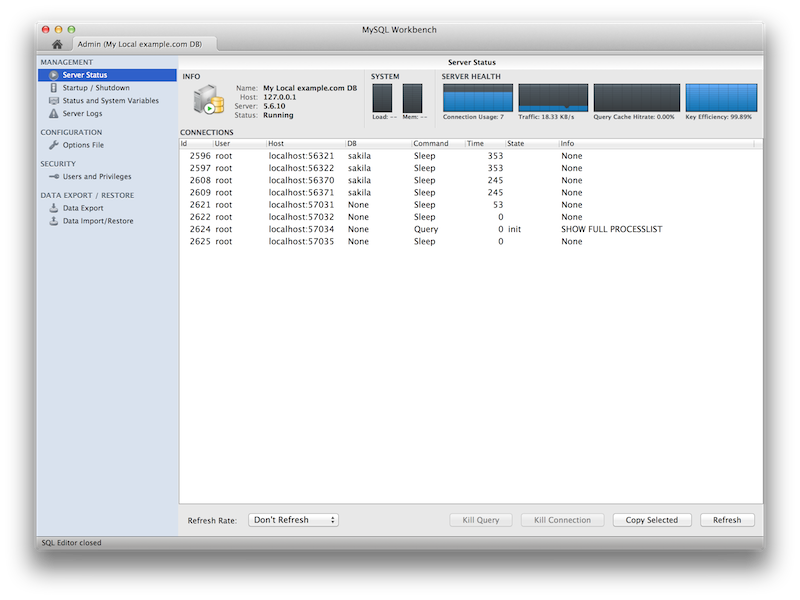
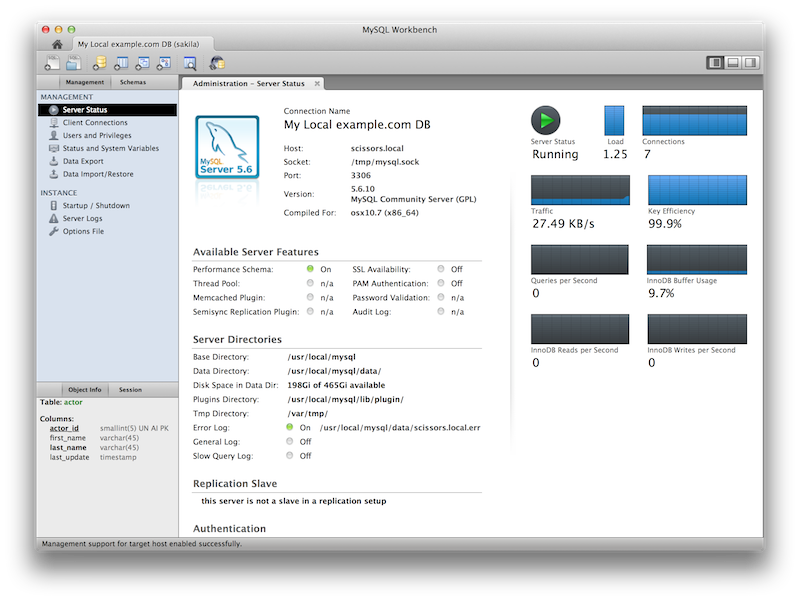
Additional server status information was added, and the user interface was improved. Select Server Status from the Management tab to open this window.
Support for MySQL Enterprise features in MySQL Workbench Commercial was added. From within the Management tab for an open connection, look for the following products under the heading MySQL Enterprise:
MySQL Enterprise Backup (MEB): A GUI front end for the MEB
tool. After installing MySQL Workbench Commercial and MySQL Enterprise Backup,
MySQL Workbench will check for and handle the prerequisites.
Backup recovery is also supported. This plugin supports MEB
with local and remote installations of Linux and macOS, and
locally for Windows.
MySQL Audit Log Inspector: A GUI for
browsing the contents of generated logs by the commercial
Audit Log Plugin. Powerful filtering and search capabilities
are available. Fast browsing is provided by caching the log
data locally in an encrypted file. This plugin supports MEB
with local and remote installations of Linux and macOS, and
locally for Microsoft Windows.