MySQL HeatWave is a fully-managed cloud service that enables organizations to efficiently run analytics, transactional processing, machine learning, generative AI, and vector processing using a single service without the need for extract, transfer, and load (ETL).
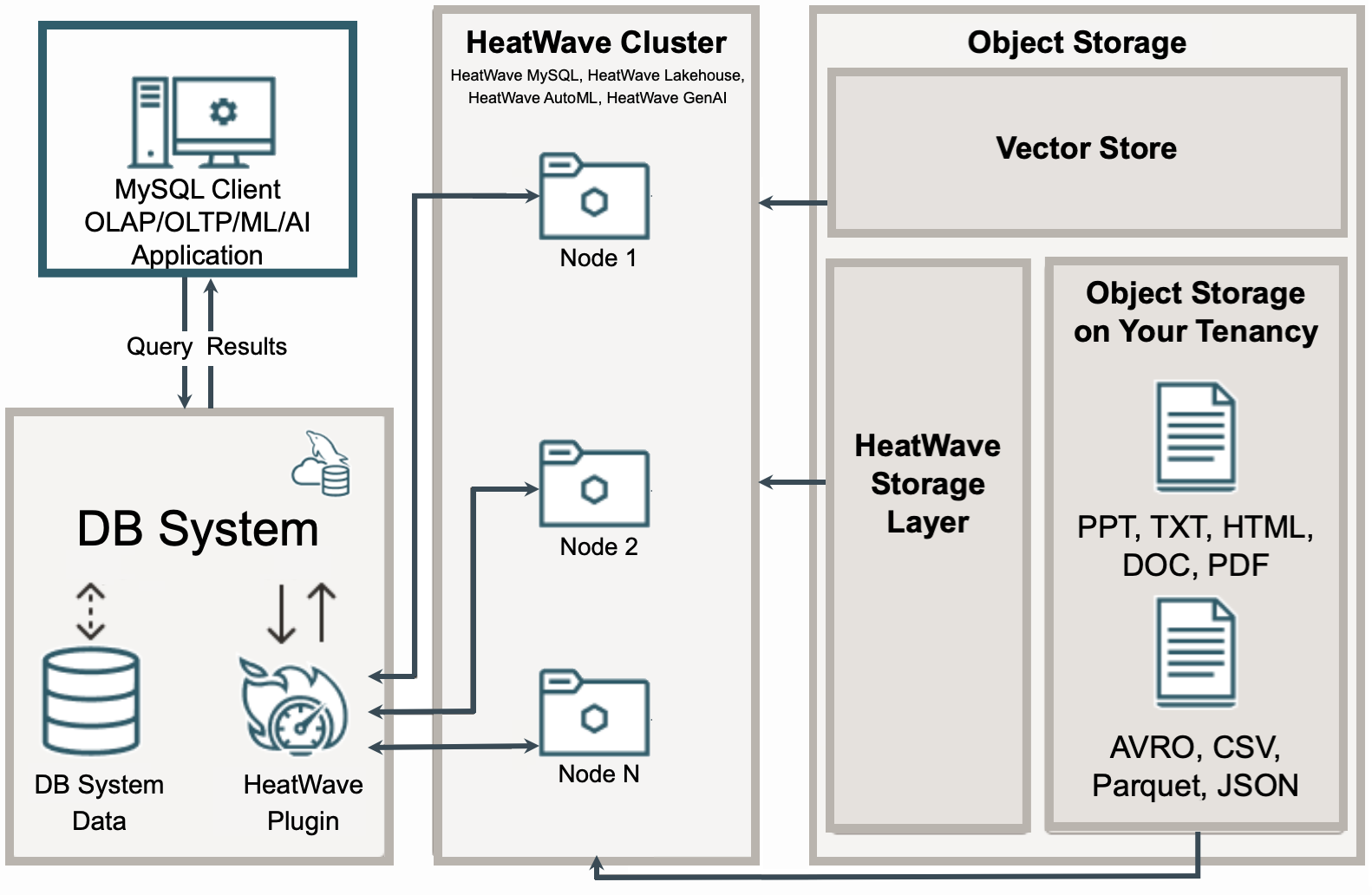
MySQL HeatWave consists of a massively parallel, high-performance, in-memory query accelerator that improves query performance by orders of magnitude. This enables organizations to efficiently perform analytical and transactional processing. The scale-out architecture of MySQL HeatWave allows loading and processing data available in the DB System as well as Object Storage, delivering unmatched performance and price-performance. It can process structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data available in Object Storage. Additionally, organizations can leverage the machine learning (ML) and generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) features of MySQL HeatWave for building predictive models, creating and enhancing AI-powered applications using proprietary data, and improving the overall data management.
The MySQL HeatWave service consists of two main components:
-
DB System
The DB System is a cloud-based Compute instance with MySQL Enterprise Edition installed. The Enterprise edition has advanced security features for encryption, data masking, authentication, and a database firewall. MySQL HeatWave is the only cloud service built on MySQL Enterprise Edition.
-
MySQL HeatWave Cluster
MySQL HeatWave Cluster serves as the in-memory accelerator that significantly enhances query performance. It also provides access to advanced machine learning (ML), generative artificial intelligence (GenAI), vector store, and Lakehouse capabilities. MySQL HeatWave Cluster consists of one or more MySQL HeatWave nodes. When data is loaded into MySQL HeatWave Cluster from the DB System or Object Storage, the data is sharded and distributed among MySQL HeatWave nodes.
MySQL HeatWave Cluster enables you to perform real-time analytics and machine learning on the structured data residing in the DB System. The traffic between the DB System and MySQL HeatWave Cluster is fully encrypted. Any changes made to the data in the DB System are automatically propagated to MySQL HeatWave Cluster, ensuring that queries always access the most up-to-date information.
MySQL HeatWave Cluster also enables you to perform analytics, machine learning, generative AI, and vector processing on the structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data residing in Object Storage. Any changes to the data in Object Storage is automatically propagated to MySQL HeatWave Cluster as well.
Data that is loaded into MySQL HeatWave Cluster is automatically persisted to the network-attached block storage, also known as MySQL HeatWave Storage Layer, which allows data to be reloaded quickly when the MySQL HeatWave Cluster resumes after a pause or when MySQL HeatWave Cluster recovers from a cluster or node failure. The vector store tables created with MySQL HeatWave GenAI also persist in the block storage.
The following design characteristics of MySQL HeatWave help deliver a compelling performance and cost advantage:
-
In-Memory Hybrid-Columnar Format
MySQL HeatWave Cluster stores data in main memory in a hybrid columnar format. The hybrid approach achieves the benefits of columnar format for query processing, while avoiding the materialization and update costs associated with pure columnar format. Hybrid columnar format enables the use of efficient query processing algorithms designed to operate on fixed-width data, and permits vectorized query processing.
-
Massively Parallel Architecture
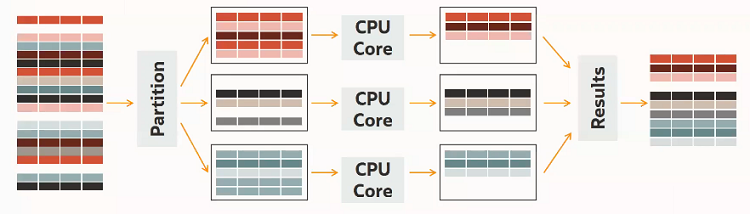
The MySQL HeatWave massively parallel architecture uses internode and intranode partitioning of data. Each node within a MySQL HeatWave Cluster, and each CPU core within a node, processes the partitioned data in parallel. MySQL HeatWave is capable of scaling to thousands of cores. This massively parallel architecture, combined with high-fanout, workload-aware partitioning, accelerates query processing.
-
Push-Based Vectorized Query Processing
MySQL HeatWave processes queries by pushing vector blocks (slices of columnar data) through the query execution plan from one operator to another. A push-based execution model avoids deep call stacks and saves valuable resources compared to tuple-based processing models.
-
Scale-Out Data Management
When data is loaded into MySQL HeatWave, the MySQL HeatWave Storage Layer automatically persists the data for pause and resume of the MySQL HeatWave Cluster and for fast recovery in case of a MySQL HeatWave node or cluster failure. Data is automatically restored by the MySQL HeatWave Storage Layer when the MySQL HeatWave Cluster resumes after a pause or recovers a failed node or cluster. This automated, self-managing storage layer scales to the size required for your MySQL HeatWave Cluster and operates independently in the background. MySQL HeatWave on OCI persists the data to OCI Object Storage. MySQL HeatWave on AWS persists the data to AWS S3.
-
Inbuilt Generative AI and Machine Learning Capabilities
MySQL HeatWave provides native generative AI and machine learning capabilities integrated directly into the database engine, eliminating the need for separate AI and ML infrastructure. This integrated approach enables organizations to perform both traditional predictive analytics and modern generative AI workloads without data movement, reducing latency and improving security while maintaining the performance benefits of in-memory processing.
-
Automated Performance Improvement
MySQL HeatWave Autopilot automates many of the most important and often challenging aspects of achieving high query performance at scale, including system setup, data loading, query execution and failure handling. It uses advanced machine learning techniques to sample data, collect statistics on data and queries, and build machine learning models to model memory usage, network load and execution time. MySQL HeatWave Autopilot uses these ML models to intelligently learn from queries executed in the system, resulting in continually improving system performance over time.
Learn about different features of MySQL HeatWave.
To learn more about the technical aspects of MySQL HeatWave, see the MySQL HeatWave Technical Brief.