A NDB Cluster is
defined as one or more MySQL Servers providing access to an
NDBCLUSTER storage engine—that
is, to a set of NDB Cluster data nodes (ndbd
processes). There are three main access paths from Java to
NDBCLUSTER, listed here:
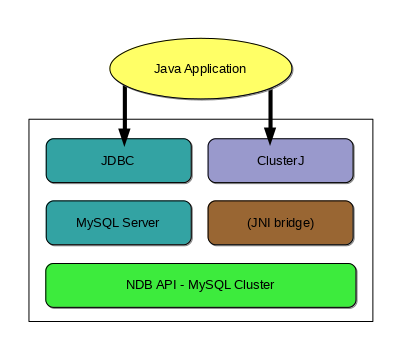
JDBC and mysqld. JDBC works by sending SQL statements to the MySQL Server and returning result sets. When using JDBC, you must write the SQL, manage the connection, and copy any data from the result set that you want to use in your program as objects. The JDBC implementation most often used with the MySQL Server is MySQL Connector/J.
Java Persistence API (JPA) and JDBC. JPA uses JDBC to connect to the MySQL Server. Unlike JDBC, JPA provides an object view of the data in the database.
ClusterJ. ClusterJ uses a JNI bridge to the NDB API for direct access to
NDBCLUSTER. It employs a style of data access that is based on a domain object model, similar in many ways to that employed by JPA. ClusterJ does not depend on the MySQL Server for data access.
These paths are shown in the following API stack diagram:
JDBC and mysqld. Connector/J provides standard access through the MySQL JDBC driver. Using Connector/J, JDBC applications can be written to work with a MySQL server acting as an NDB Cluster SQL node in much the same way that other Connector/J applications work with any other MySQL Server instance.
For more information, see Section 4.2.3, “Using Connector/J with NDB Cluster”.
ClusterJ.
ClusterJ is a native Java Connector for
NDBCLUSTER (or
NDB), the storage engine for NDB
Cluster, in the style of
Hibernate,
JPA,
and
JDO.
Like other persistence frameworks, ClusterJ uses the
Data
Mapper pattern, in which data is represented as domain
objects, separate from business logic, mapping Java classes to
database tables stored in the
NDBCLUSTER storage engine.
The NDBCLUSTER storage engine is
often referred to (in MySQL documentation and elsewhere) simply
as NDB. The terms
NDB and NDBCLUSTER are
synonymous, and you can use either ENGINE=NDB
or ENGINE=NDBCLUSTER in a
CREATE TABLE statement to create
a clustered table.
ClusterJ does not need to connect to a mysqld
process, having direct access to
NDBCLUSTER using a JNI bridge that is
included in the dynamic library libnbdclient.
However, unlike JDBC, ClusterJ does not support table creation and
other data definition operations; these must be performed by some
other means, such as JDBC or the mysql client.
Also, ClusterJ is limited to queries on single tables, and does
not support relations or inheritance; you should use another kind
of access paths if you need support for those features in your
applications.