After installing the MySQL Cluster Manager Agent as a Windows service, you can start and stop the agent using the Windows Service Manager. The installation also configures the agent to start automatically whenever Windows starts, and to shut down safely whenever Windows shuts down.
The Windows service can be used to control the running of
MySQL Cluster Manager agents on a single host only. To shut down agents on
multiple hosts, you can use the stop
agents command in the MySQL Cluster Manager client.
The installation is performed using the command prompt (cmd.exe); as with installing or removing any Windows service, it must also be done as a user having sufficient permissions, such the system Administrator account.
If the account you are currently using has Administrator
privileges, you can simply start
cmd.exe. Otherwise, you must
run the command prompt program as the Administrator. To do
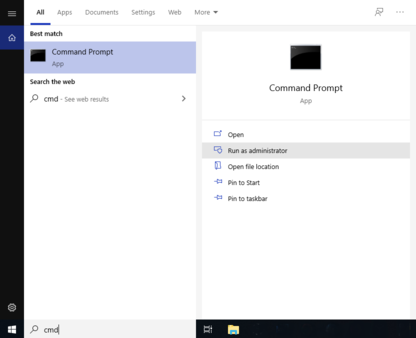
this, first locate a shortcut to the command prompt. You can
do this by typing cmd into the search
box in the Windows Taskbar, and then
select from the search results > . You can see how this looks on a
typical Windows system in the next figure.
If a Windows UAC dialog referring to cmd.exe appears, click to allow the command prompt to run as Administrator and thus to continue. You should now have a command prompt window open on your desktop, running a session with Administrator privileges.
To install the MySQL Cluster Manager agent as a service, we use the
SC CREATE command. This command allows us
to specify a name for the service (for use with SC
START and SC STOP or NET
START and NET STOP commands), a
display name (to be shown in the Service Manager), a startup
mode (automatic or manual start), and a path to the executable
to be run as a service (use mcmd-svc.exe
rather than mcmd.exe as the executable).
The path must also include any arguments needed by the
program; in the case of MySQL Cluster Manager,
mcmd-svc.exe must be told
where to find its configuration file by the
--defaults-file option. Both of
these paths must be absolute.
Installation of the MySQL Cluster Manager agent as a service is recommended. However, you should not install MySQL NDB Cluster processes (ndb_mgmd.exe, ndbd.exe, ndbmtd.exe, mysqld.exe) as services on Windows hosts to be used as MySQL NDB Cluster nodes under management by MySQL Cluster Manager, since the MySQL Cluster Manager agent itself controls MySQL NDB Cluster nodes independently of the Windows Service Manager.
Assume that you have installed MySQL Cluster Manager to the default location
for 32-bit Windows systems C:\Program Files
(x86)\MySQL\MySQL Cluster Manager (C:\Program
Files\MySQL\MySQL Cluster Manager\ on 64-bit Windows systems), and
that its configuration file is located in C:\Program
Files (x86)\MySQL\MySQL Cluster
Manager\mcm1.4.8\etc\; then, the following command
installs MySQL Cluster Manager as a service named MCM, with
the display name “MySQL Cluster Manager 1.4.8”:
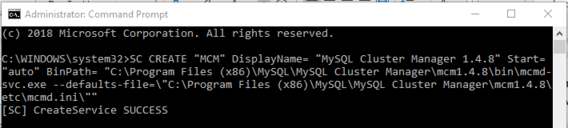
SC CREATE "MCM" DisplayName= "MySQL Cluster Manager 1.4.8" Start= "auto"
BinPath= "C:\Program Files (x86)\MySQL\MySQL Cluster Manager\mcm1.4.8\bin\mcmd-svc.exe
--defaults-file=\"C:\Program Files (x86)\MySQL\MySQL Cluster Manager\mcm1.4.8\etc\mcmd.ini\""This command can be quite long. For enhanced legibility, we have broken it across several lines, but you should always enter it on a single line, allowing it to wrap naturally, similar to what is shown here:
In addition, you should keep in mind that the spaces after the
equal signs following the DisplayName,
Start, and BinPath
arguments are required.
Starting and stopping the MySQL Cluster Manager agent Windows service.
After installing the service successfully, you can start and
stop the service manually, if the need arises, with the
SC START and SC STOP
commands.
C:\>SC START MCM
C:\>SC STOP MCM
Alternatively, use the NET START and
NET STOP commands:
C:\Windows\system32>NET START MCM
C:\Windows\system32>NET STOP MCM
Once the service is installed, the MySQL Cluster Manager agent starts
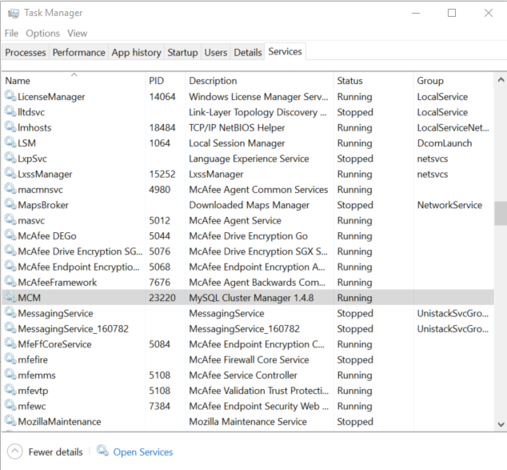
automatically whenever Windows is started. You can verify that
the service is running with the Windows Task Manager. Open the
Task Manager, and switch to the Services
tab if it is not already displayed. If the MySQL Cluster Manager agent is
running, you can find it in the list of services under
MCM in the Name, column
and MySQL Cluster Manager 1.4.8 in the
Description column, as shown here:
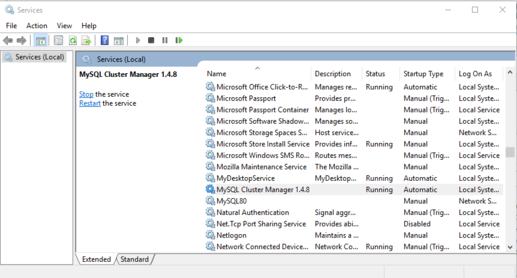
You can also verify if the service is running using the Windows Service Manager, as shown here:
The Service Manager also allows you to start, stop, or pause the MySQL Cluster Manager agent service manually using a GUI.
When first installing the MySQL Cluster Manager agent as a service, the
service is not started automatically until Windows is
started. If you do not wish to restart Windows, then you
must start the service manually using either SC
START or NET START on the
command line or the graphical control provided in the
Windows Service Manager.
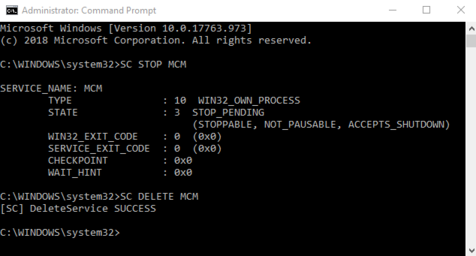
You can remove the service using the SC
DELETE command and the name of the service—in
this case MCM—that was used in the
SC CREATE command, as shown here:
If the service is running at the time that SC
DELETE is executed, the removal of the service takes
effect the next time the service is stopped. In such a case,
you must stop the previous instance of the service manually,
and allow it to be removed, before you can reinstall the
service.
Once you have installed the MySQL Cluster Manager agent and the service is running correctly, you are ready to connect to it using the MySQL Cluster Manager client. See Section 3.3, “Starting the MySQL Cluster Manager Client”, for information about how to do this.