Table of Contents
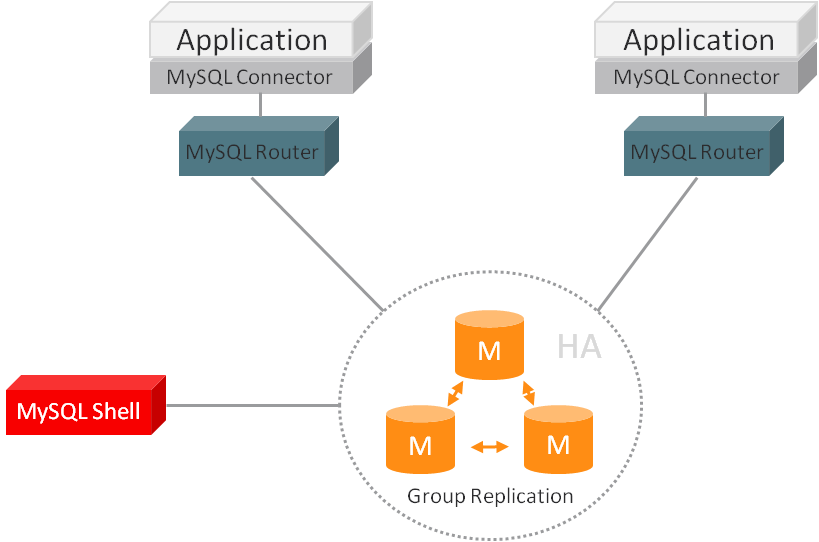
Performance Recommendations
For best performance, MySQL Router is typically installed on the same host as the application that uses it. Possible reasons include:
-
To allow local UNIX domain socket connections to the application, instead of TCP/IP.
NoteUnix domain sockets can function with applications connecting to MySQL Router, but not for MySQL Router connecting to a MySQL Server.
To decrease network latency.
To allow MySQL Router to connect to MySQL without requiring extra accounts for the Router's host, for MySQL accounts that are created specifically for application hosts such as myapp@198.51.100.45 instead of a value like myapp@%.
Typically application servers are easiest to scale.
You can run multiple MySQL Router instances on your network, and you do not need to isolate MySQL Router to a single machine. This is because MySQL Router has no affinity for any particular server or host.