MySQL (part of Sun Microsystems) have just announced the release of MySQL Cluster 7.0. This is a major new version of the database.
The highlights of the release (as well as an overview of the MySQL Cluster architecture) have been published in a new white paper: MySQL Cluster 7.0: Architecture and New Features.
For those in a rush, here are the highlights of the highlights:
- Multi-threaded data nodes. Could previously exploit up to 2 cores/CPUs/threads for a single data node. This is extended to 8 cores by introducing a multi-threaded version of the ndb process. This delivers a very significant performance improvement if running on a host with more than a dual core.
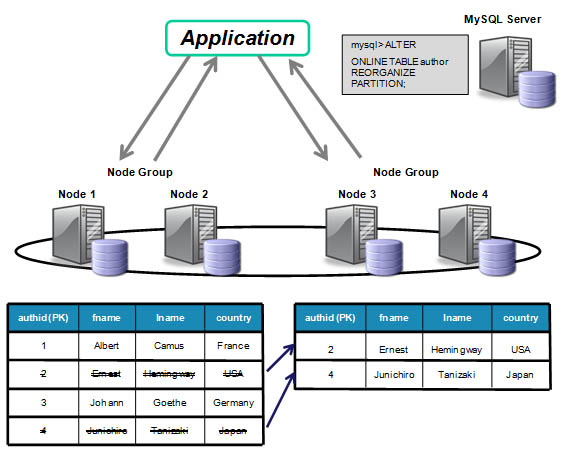
- On-line add node. The ability to add a new node group to an in-service Cluster without impacting service. Includes the ability to repartition the data in existing tables after the new node group has been added.
- Carrier-Grade directory back end. Support for using MySQL Cluster as the data store for a directory server. Allows LDAP access to your data. OpenLDAP will be the first directory to release a driver for this.
- Multi-Threaded Disk Data File Access. Improves the performance for disk-based table data.
- Improved large record handling. Performance/network bandwidth improvements.
- Alpha version of a Windows port. Intended for development use only, not for deployment.
- Snapshot option for backups. Option to have the backup represent the state of the database at the point that the backup was started rather than when it finished. This lets you synchronise it with other, external events such as the backing up of other databases.
- Caching of configuration data. When a node restarts, it will only adopt any changes to the config files if explicitly told to – avoiding the situation where one node restarts and ends up with different config data to the others.
- Transactions for schema changes. Safer way to update the schema that can tolerate node failures mid-operation.