MySQL REST Service - Quickstart Guide
This book provides a hands-on approach to learning how to use the MySQL REST service. It shows how to set up and work with REST endpoints for MySQL database objects.
Chapter Overview
- What is the MySQL REST Service
- Setting up the MySQL REST Service
- Defining REST Endpoints
- Accessing REST Endpoints
- Appendix
Please also see
- MySQL REST Service - Reference Manual - This book contains the documentation for the MySQL REST Service (MRS).
- MySQL REST Service - Core REST APIs - This book provides examples of using the MySQL REST Service queries and other operations against tables and views after you have REST-enabled them.
- MySQL REST Service - SQL Reference - This book discusses the MySQL REST Service SQL Extension.
- MySQL REST Service - SDK Reference - This book explains how to work with the MRS Software Development Kit and discusses the Client APIs.
1 Quickstart Introduction
Welcome to the MySQL REST Service (MRS). It provides a fast and powerful way to serve JSON documents to client applications via a HTTPS REST interface.
To learn more about the MySQL REST Service please check out the Developer Guide.
2 Setting up the MySQL REST Service
To get started with the MySQL REST Service, you must first deploy a MySQL solution. In this guide, we will use a local MySQL Server installation. If you have an existing MySQL server or InnoDB ClusterSet installed, you can use that setup instead. This is also true if you are working with a HeatWave instance.
2.1 Setting up a local MySQL Server
Please go to the MySQL download page and select a MySQL Server version. It is recommended to download the latest MySQL Innovation or LTS release. Download the appropriate packages for your local operating system and perform the local installation either on MacOS, Linux or Windows.
After the MySQL Server has been installed, make sure that it is started up and that a database connection can be established, using the MySQL Shell for VS Code extension.
2.2 Setting up VS Code
The recommended way to configure a MySQL REST Service development setup is to use VS Code or VSCodium with the MySQL Shell for VS Code extension installed.
After downloading and installing VS Code, select the
Extensions icon in the Activity Bar on the left hand
side and enter MySQL Shell, then click the
Install button.
When using VSCodium, please see here how to enable the
MS Marketplace first. With the MS Marketplace
enabled, select the Extensions icon in the Activity Bar
on the left hand side, enter MySQL Shell and then click
the Install button.
2.2.1 MySQL Shell Welcome Wizard
When first launching the MySQL Shell VS Code extension, a Welcome Wizard will be shown. Please follow the required steps to configure the extension.
In case of an issue, the extension can be reset by
bringing up the VS Code Command Palette and selecting
the Reset MySQL Shell for VS Code Extension
or by selecting the corresponding popup menu item of the
DATABASE CONNECTIONS view in the Primary
Side Bar.
2.2.2 Adding a DB Connection
After successfully configuring the MySQL Shell VS
Code extension, select its icon in the VS Code Activity
Bar on the left hand side. Then click the
DB Connection Overview entry in the
OPEN EDITORS view in the Primary Side
Bar.
On the DB Connection Overview page,
click the New Connection tile in the
Database Connections list. This will bring
up the Database Connection Configuration
dialog.
- Choose a
Captionfor the new DB Connection, e.g.MRS Development. - Set the
User Nametoroot - Click
OKto create the DB Connection.
A new DB Connection tile will show up in the
DB Connection Overview, as well as a new DB
Connection entry in the
DATABASE CONNECTIONS view in the Primary
Side Bar.
2.2.3 Opening a DB Connection
Click the new tile to open the database connection. Enter the password and select whether to store it.
A new DB Notebook page will be opened,
showing an SQL prompt.
2.3 Configuring a MySQL Instance for MySQL REST Service Support
Support for the MySQL REST Service has to be explicitly configured on a given MySQL setup, before it can be used.
This configuration can either be performed directly in the MySQL Shell for VS Code extension or via the REST SQL extension available in the MySQL Shell.
When using a HeatWave setup on OCI, please browse the HeatWave documentation on how to enable REST service support for the given HeatWave instance.
2.3.1 Configuring MRS in MySQL Shell for VS Code
Using the MySQL Shell for VS Code extension, locate
the DATABASE CONNECTIONS view in the
Primary Side Bar and right-click on the DB Connection
entry MRS Development created above. This
will bring up the popup menu.
Select
Configuring Instance for MySQL REST Service Support
in the DB Connection’s popup menu, which will bring up
the MySQL REST Service dialog.
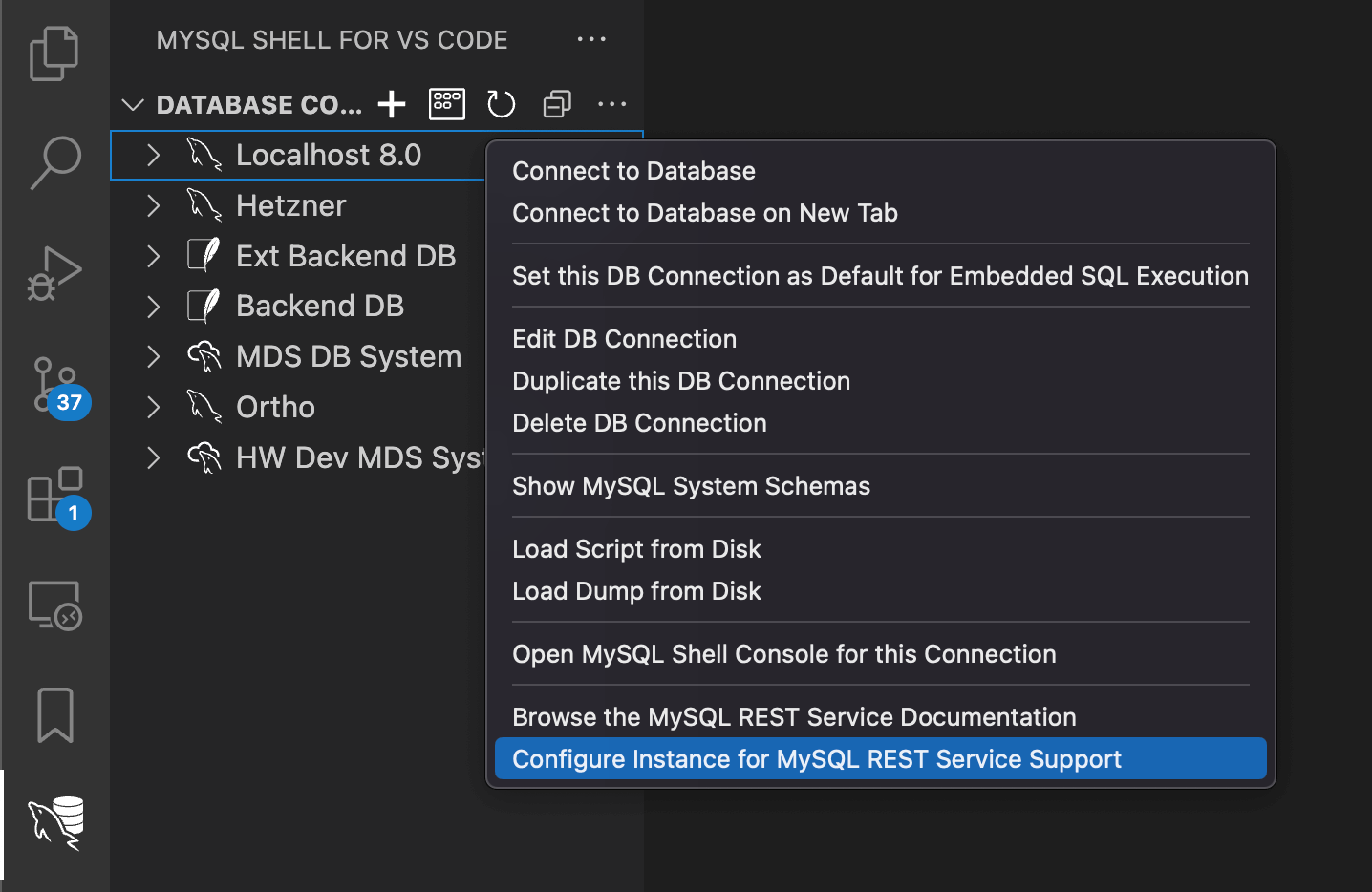
On the MySQL REST Service dialog provide
a REST User Name and a
REST User Password. Please note that the
password has a minimum length of 8 characters and must
contain a lower case character, and upper case
character, a number and a special character. The REST
user specified on this dialog can later be used to log
into REST services.
Click OK to configure the instance for
MySQL REST Service support. This process will create a
dedicated metadata schema on the MySQL instance, which
holds all metadata information about the REST services
and endpoints.
After MySQL has been configured for MySQL REST
Service support, a new MySQL REST Service
child entry can be seen when expanding the DB Connection
entry in the DATABASE CONNECTIONS view in
the Primary Side Bar.
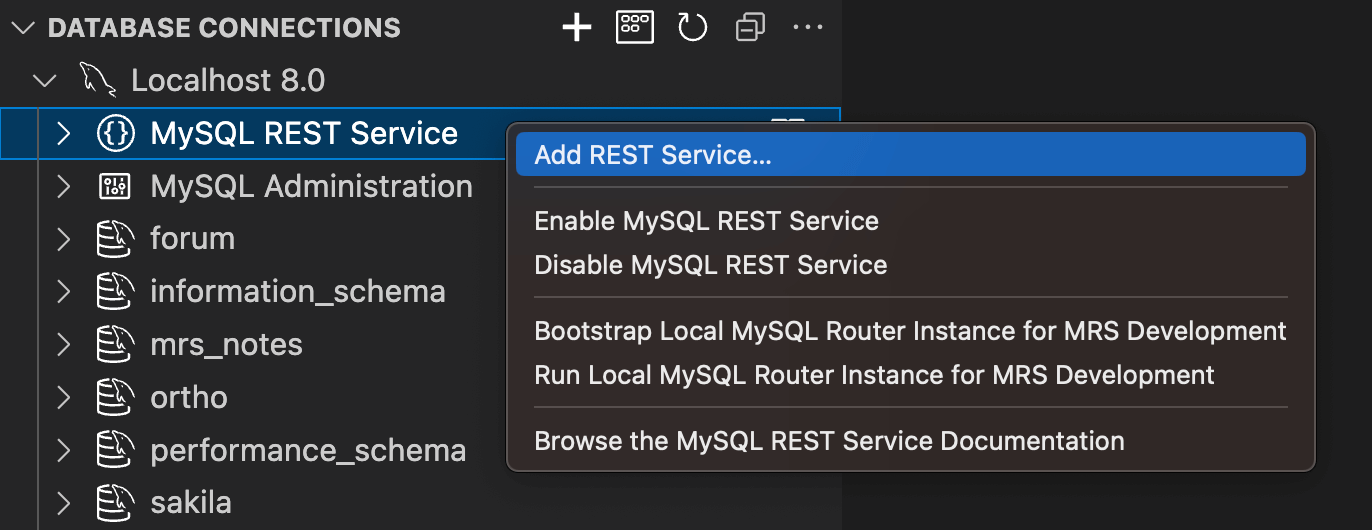
2.3.2 Adding the MRS Authentication App for HeatWave
When you are working against a HeatWave instance, the REST user mentioned above needs to be created explicitly.
Open the MySQL REST Service child entry
of the DB Connection, click on the
REST Authentication Apps item with the
right mouse button and select
Add New Authentication App.
This will show the
REST Authentication App dialog. Select the
vendor MRS and click OK to
have the new REST authentication app be created.
Expand the REST Authentication Apps item
in the tree view and right click on the new
MRS entry. Select Add User
from the popup menu when clicking the MRS
entry with the right mouse button.
Provide a User Name and a
User Password and click OK to
have the REST user created.
2.4 Assigning REST User Privileges
When working with MySQL, it is recommended that the
root account be used exclusively for
configuration purposes. Create dedicated MySQL user
accounts for general administrative and development
tasks instead.
2.4.1 DBA Account
When working with HeatWave, a dedicated MySQL user account with administrative privileges was already created during HeatWave deployment. This MySQL user account can be used instead. Please proceed to Granting REST Service Admin Privileges.
To create a database administrator account named
dba the following SQL commands can be
used.
This account will have full privileges on all
database schemas. To adjust the list of schemas, modify
the GRANT ALL ON *.* statement
accordingly.
CREATE USER 'dba'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY '********';
GRANT ALL ON *.* TO 'dba'@'%' WITH GRANT OPTION;After creating the new account, remember to update
the DB Connection and replace the User Name
root with dba. This can be
done by clicking on the DB Connection entry with the
right mouse button and selecting
Edit DB Connection.
2.4.2 Granting REST Service Admin Privileges
Any existing MySQL user account can be promoted to a
REST service administrator by granting the
mysql_rest_service_admin role. This role
has to be added to the default MySQL roles that are
assigned when a MySQL user connects.
The following two statements grant the required MySQL role and assign all roles to be loaded by default.
GRANT 'mysql_rest_service_admin' TO 'dba'@'%';
SET DEFAULT ROLE ALL TO 'dba'@'%';Please note that the
mysql_rest_service_adminrole is only available after configuring the MySQL instance for MySQL REST Service support.
The MySQL REST Service supports several MySQL roles to manage fine-grained access for administrators and developers. Please check the MRS User Roles documentation for more details.
2.5 Deploying a MySQL Router for Development
When developing REST services, it is highly recommended to deploy a local MySQL Router instance. This allows developers to locally test the REST services they are working on without publishing them on the production systems. Please see the REST Service Lifecycle Management for details.
To bootstrap and start a local MySQL Router in
development mode, select
Bootstrap Local MySQL Router Instance from
the MySQL REST Service items popup
menu.
A terminal will appear.
- Enter the password of the MySQL user and hit the
returnkey. - Next, enter a JWT secret. Since this is a local
development server, a simple secret like
1234can be used. Please note that the same, strong JWT secret has to be used on all production routers.
Now, a local development instance of the MySQL Router has been bootstrapped.
Select Start Local MySQL Router Instance
from the MySQL REST Service items popup
menu to start up the router.
The terminal will display the MySQL Router log output in real time. This log output is very helpful when debugging REST endpoints.
3 Defining REST Endpoints
After configuring a MySQL instance for MySQL REST Service support, you can define new REST services and endpoints. This can be done using the graphical user interface built into the MySQL Shell extension for Visual Studio Code or directly via the MySQL Shell REST SQL extension.
3.1 Deploying the Sakila Schema
All further examples in the quickstart guide use the
Sakila example database schema. To follow
along, please install that schema.
- Download the Sakila schema from https://downloads.mysql.com/docs/sakila-db.zip
- Double-click the downloaded ZIP file to extract it.
This will create a folder
sakila-dbcontaining two SQL scripts. - Using the MySQL Shell for VS Code extension, locate
the
DATABASE CONNECTIONSview in the Primary Side Bar and right-click on the DB Connection entryMRS Developmentcreated above. From the popup menu selectLoad SQL Script from Disk...and select thesakila-schema.sqlscript. - After the script has loaded, click the first
lightning bolt in the toolbar to execute the full
script. Monitor the output until the line
✓ SQL Script execution completed in ___s. 46 statements executed successfully.is displayed. - Use
Load SQL Script from Disk...again and select thesakila-data.sqlscript. Execute it and monitor the output for✓ SQL Script execution completed in ___s. 62 statements executed successfully.
The sakila schema should now be
displayed in the DATABASE CONNECTIONS view
in the Primary Side Bar as a child entry of the
MRS Development connection.
3.2 Creating a REST Service
To create a REST service, click with the right mouse
button on the MySQL REST Service child
entry of the MRS Development connection in
the DATABASE CONNECTIONS view in the
Primary Side Bar.
This will bring up the
MySQL REST Service dialog. You can set a
REST service path and a REST Service Name or accept the
defaults of /myService for now.
The REST service will be created without being
Published and the REST authentication app
MRS will be linked by default. To also
allow logins with MySQL user accounts, the REST
authentication app MySQL can be linked as
well.
Click OK to have the REST service
created.
The new REST Service will now be displayed as a child
to the MySQL REST Service item in the tree
view.
3.2.1 Creating a REST Service with REST SQL
Alternatively to using the graphical user interface the REST SQL extension can be used to create the REST service.
CREATE OR REPLACE REST SERVICE /myService
ADD AUTH APP 'MRS';3.3 Adding a REST Endpoint
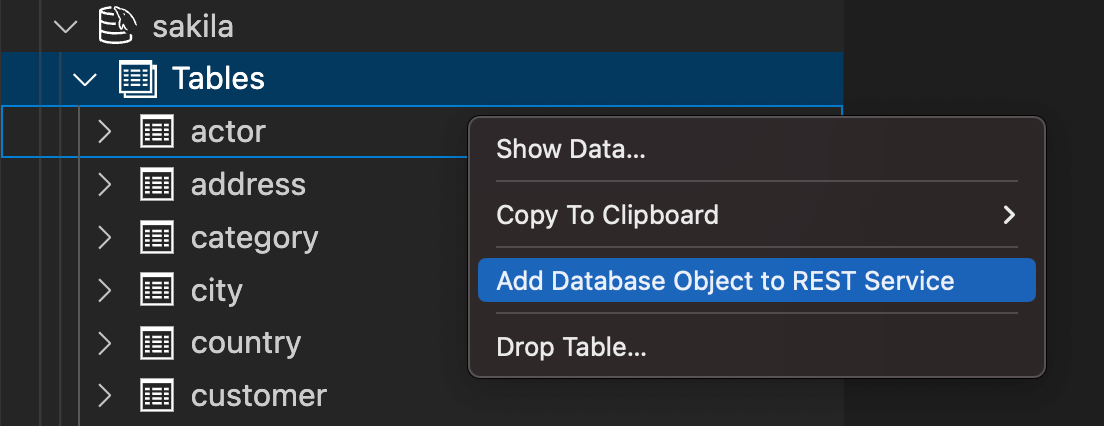
After a REST service has been created, a new REST endpoint can be added. It is possible to add database schema tables, views, procedures and functions, as well as static files.
On the DATABASE CONNECTIONS view in the
Primary Side Bar, expand the sakila
database schema tree item as well as the
Tables item of the DB Connection entry.
Click the database schema table city
using the right mouse button and select
Add Database Object to REST Service from
the popup menu.
A notification will be show on the lower right area of the window displaying the following question.
The database schema sakila has not been added to the REST service.
Do you want to add the schema now?Before adding a database schema object as a REST
endpoint, it is required to add their database schema as
a REST schema first. Click Yes to add the
database schema as a REST schema.
The MySQL REST Object dialog will be
displayed.

It shows the full request path that will be used for
the REST endpoint, consisting of the parts
REST Service Path
REST Schema Path
REST Object Path. In this case the path
will be /myService/sakila/city.
Since we want this REST endpoint to not require authentication, disable the
Auth. Requiredoption in theAccess Controlsection, top right.
On the Data Mapping tab sheet, the
mapping of JSON fields to database columns can be seen.
It is possible to rename JSON fields or add referenced
tables as nested JSON documents. See Data Mapping
Views for more details.
To enable write access on the REST endpoint, click
the INSERT UPDATE
DELETE buttons next to the database schema
name.
Click OK to create the REST
endpoint.
3.3.1 Adding a REST Endpoint via REST SQL
The same operations as doing in the user interface above can also be done via the REST SQL extension.
In a first step, the database schema can be added to the REST service as a REST schema.
CREATE OR REPLACE REST SCHEMA /sakila ON SERVICE /myService
FROM `sakila`;Next, the sakila.city database schema
table can be added.
CREATE OR REPLACE REST VIEW /city ON SERVICE /myService SCHEMA /sakila
AS `sakila`.`city` @INSERT @UPDATE @DELETE
AUTHENTICATION NOT REQUIRED;4 Accessing REST Endpoints
A MySQL Router instance must be used to access any REST endpoint. When developing on a REST service, please make sure to deploy a MySQL Router in development mode.
4.1 Web Browser Access
To access a REST endpoint, expand the REST service
entry in the DATABASE CONNECTIONS tree view
until you reach the REST object. Right-click on
city REST endpoint and select
Open REST Object Request Path in Web Browser
from the popup menu.
This will open up a web browser pointing at the REST
endpoint URL
https://localhost:8443/myService/sakila/city
and display the JSON document returned from accessing
the REST endpoint via the GET method.
The port number of the URL depends on the internal ID of the DB Connection and is different for each connection.
{
"items": [
{
"city": "A Coruña (La Coruña)",
"links": [
{
"rel": "self",
"href": "/myService/sakila/city/1"
}
],
"cityId": 1,
"countryId": 87,
"lastUpdate": "2006-02-15 04:45:25.000000",
"_metadata": {
"etag": "09785343A8A790724C995E20AE6844EA2A78E9CFD57BE64063B2FC56E12D8FFC"
}
},
{
"city": "Abha",
"links": [
{
"rel": "self",
"href": "/myService/sakila/city/2"
}
],
"cityId": 2,
"countryId": 82,
"lastUpdate": "2006-02-15 04:45:25.000000",
"_metadata": {
"etag": "B069A2EEC4663506F97019A369BD77AB086A9BA5FB1DD224C36B67CF687A6B14"
}
},
...
],
"limit": 25,
"offset": 0,
"hasMore": true,
"count": 25,
"links": [
{
"rel": "self",
"href": "/myService/sakila/city/"
},
{
"rel": "next",
"href": "/myService/sakila/city/?offset=25"
}
]
}4.2 TypeScript Prompt
The MySQL Shell for VS Code supports and interactive workflow to prototype REST access using TypeScript.
After opening a database connection in MySQL Shell
for VS Code the DB Notebook will be displayed. Switch
the DB Notebook to TypeScript mode with \ts
if it is in SQL mode.

First, you can check the status of the MySQL REST
Service by executing the mrs.getStatus();
command. Since the automatically generated Client SDK is
fully type safe, auto completion support will be
provided all the way.
ts> mrs.getStatus();
{
"configured": true,
"info": "1 REST service available.",
"services": [
{
"serviceName": "myService",
"url": "https://localhost:8443/myService",
"isCurrent": true
}
]
}Next we can do a findFirst() operation
on the /myService/sakila/city endpoint to
fetch the first city in the list. Again, the auto
completion feature should guide the way.
ts> myService.sakila.city.findFirst();
{
"city": "A Coruña (La Coruña)",
"cityId": 1,
"countryId": 87,
"lastUpdate": "2006-02-15 04:45:25.000000"
}Searching for a specific city can be done by using
the find() method and using a where
clause.
ts> myService.sakila.city.find({where: {city: { '$like': 'Van%'}}})
[
{
"city": "Vancouver",
"cityId": 565,
"countryId": 20,
"lastUpdate": "2006-02-15 04:45:25.000000"
}
]Many more methods are available when using the Client SDK. Please see the SDK Reference for more details.
4.3 Access via CURL
Instead of using a web browser, the REST endpoint can be accessed using any other HTTP client as well.
Using curl is a popular way to fetch
data via HTTP from the command line. It is installed by
default on MacOS machines and can easily be installed on
Linux and Windows.
To access the city REST endpoint, the following can be executed on a terminal. The JSON data will be formatted using the jq tool.
curl -s "https://localhost:8443/myService/sakila/city" | jq
{
"items": [
{
"city": "A Coruña (La Coruña)",
"links": [
{
"rel": "self",
"href": "/myService/sakila/city/1"
}
],
"cityId": 1,
"countryId": 87,
"lastUpdate": "2006-02-15 04:45:25.000000",
"_metadata": {
"etag": "09785343A8A790724C995E20AE6844EA2A78E9CFD57BE64063B2FC56E12D8FFC"
}
},
{
"city": "Abha",
"links": [
{
"rel": "self",
"href": "/myService/sakila/city/2"
}
],
"cityId": 2,
"countryId": 82,
"lastUpdate": "2006-02-15 04:45:25.000000",
"_metadata": {
"etag": "B069A2EEC4663506F97019A369BD77AB086A9BA5FB1DD224C36B67CF687A6B14"
}
},
...
],
"limit": 25,
"offset": 0,
"hasMore": true,
"count": 25,
"links": [
{
"rel": "self",
"href": "/myService/sakila/city/"
},
{
"rel": "next",
"href": "/myService/sakila/city/?offset=25"
}
]
}To perform a find operation we can specify the
additional q parameter. To learn more about
the core REST API syntax please browse the corresponding
Core REST
APIs manual.
url=https://localhost:8443/myService/sakila/city
curl -s "$url?q=$(echo '{"city":{"$like":"Van%"}}'|jq -sRr @uri)" | jq
{
"items": [
{
"city": "Vancouver",
"links": [
{
"rel": "self",
"href": "/myService/sakila/city/565"
}
],
"cityId": 565,
"countryId": 20,
"lastUpdate": "2006-02-15 04:45:25.000000",
"_metadata": {
"etag": "E5162E0999E4A016B8AEA25FE6E5C79C6F171B3A207B4143C20B1D3380C6BABA"
}
}
],
"limit": 25,
"offset": 0,
"hasMore": false,
"count": 1,
"links": [
{
"rel": "self",
"href": "/myService/sakila/city/"
}
]
}4.4 Deploying a Web App
The MySQL REST Service not only serves dynamic database schema data, but also static files. This feature can be used to upload a Progressive Web App (PWA) and have the MySQL Routers serve the PWA. In that case, no additional web server setup is needed.
One popular PWA is the OpenAPI Web UI (also called SwaggerUI). It provides a user friendly interface to work with REST endpoints based on their OpenAPI definition.
To deploy a OpenAPI Web UI instance for the REST
service created above, right click on the REST service
item DATABASE CONNECTIONS view and select the
Deploy OpenAPI Web UI popup menu item.
Please note that this operation requires an internet connection that can reach
github.com.
This will show the MRS Content Set
dialog. Leave all settings unchanged and click the
OK button.
The OpenAPI Web UI will now be downloaded from
github.com, patched with a dark mode and
enabling authentication with MRS. After this operation
is completed, a notification will be show stating
The MRS static content set has been added successfully. 10 files have been uploaded.
Now, navigate to the REST service item DATABASE
CONNECTIONS view and right-click on the
/OpenApiUi REST content set item. Select
the
Open Content Set Request Path in Web Browser
popup menu item.
This will open the URL
https://localhost:8443/myService/openApiUi/
in a web browser and render the OpenAPI Web UI for the
/myService, giving access to the different
HTTP methods for the /myService/sakila/city
endpoint.
5 Quickstart Appendix
5.1 Enabling MS Marketplace on VSCodium
In order to use extensions from the MS Marketplace on VSCodium, a configuration file has to be created.
Open an editor of your choice and paste the following content.
{ "nameShort": "Visual Studio Code", "nameLong": "Visual Studio Code", "extensionsGallery": { "serviceUrl": "https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/_apis/public/gallery", "cacheUrl": "https://vscode.blob.core.windows.net/gallery/index", "itemUrl": "https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items" } }Save the file at the following location.
- MacOS:
$HOME/Library/Application Support/VSCodium/product.json - Windows:
$HOME\AppData\Roaming\VSCodium\product.json
- MacOS:
Restart VSCodium.
To revert to using VSCodium’s default marketplace, simply delete the project.json file and restart VSCodium.
Copyright (c) 2025, 2026, Oracle and/or its affiliates.